Symmetric Algorithm
Principle
Theencryptionanddecryptionofthesymmetricalgorithmisexpressedas:
Ek(M)=C
Dk(C)=M
Symmetricalgorithmscanbedividedintotwocategories.Analgorithmthatonlyoperatesonasinglebit(sometimesabyte)intheplaintextatatimeiscalledasequencealgorithmorasequencecipher.Anothertypeofalgorithmistoperformoperationsonagroupofbitsintheplaintext.Thesegroupsofbitsarecalledgrouping,andthecorrespondingalgorithmiscalledagroupingalgorithmorablockcipher.Thetypicalpacketlengthofmoderncomputercryptographicalgorithmsis64bits-thislengthislargeenoughtopreventanalysisanddeciphering,butsmallenoughtofacilitateitsuse.
Thisalgorithmhasthefollowingcharacteristics:
Dk(Ek(M))=M
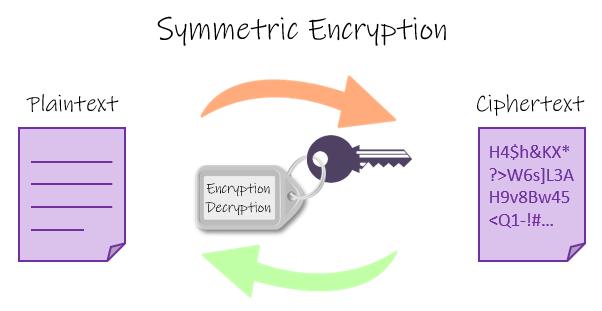
Thereare5commonlyusedencryptionschemesusingsymmetriccryptographyComponents:
1)Plaintext:originalinformation.
2)Encryptionalgorithm:Usethekeyasaparametertoperformmultiplereplacementandconversionrulesandstepsontheplaintext,andtheresultoftheconversionisciphertext.
3)Key:Theparametersofencryptionanddecryptionalgorithmsdirectlyaffecttheresultoftransformingtheplaintext.
4)Ciphertext:Theresultoftransformingtheplaintext.
5)Decryptionalgorithm:Inversetransformationofencryptionalgorithm,withciphertextasinputandkeyasparameters,andthetransformationresultisplaintext.
Features
Theadvantagesofsymmetriccryptographyarehighefficiency(encryption/decryptionspeedcanreachtensofmegabytespersecondormore),simplealgorithm,lowsystemoverhead,suitableforlargenumbersofencryptiondata.
Defects
Althoughsymmetriccryptographyhassomegoodcharacteristics,italsohasobviousdefects,including:
l)BeforeconductingsecurecommunicationThekeyexchangeneedstobedoneinasecuremanner.Thisstepisfeasibleundercertaincircumstances,butundercertaincircumstancesitwillbeverydifficultorevenimpossibletoachieve.
2)Complexscale.Forexample,thekeybetweenAandBmustbedifferentfromthekeybetweenAandC,otherwisethesecurityofthemessagetoBwillbethreatened.Inagroupof1000users,Aneedstokeepatleast999keys(moreprecisely,1000,ifsheneedstoleaveakeyforhimselftoencryptdata).Forotherusersinthegroup,thissituationalsoexists.Inthisway,thisgrouprequiresatotalofnearly500,000differentkeys!Byextension,agroupofnusersrequiresN2/2differentkeys.
Byapplyingacentralservicestructurebasedonsymmetriccryptography,theabove-mentionedproblemshavebeenalleviated.Inthissystem,anyuserinthegroupsharesakeywithacentralserver(usuallycalledakeydistributioncenter).Therefore,thenumberofkeysthatneedtobestoredisbasicallythesameasthenumberofpeopleinthegroup,andthecentralservercanalsoactasan"introducer"foruserswhodidnotknoweachotherbefore.However,thiscentralserver,whichiscloselyrelatedtosecurity,mustbeonlineatalltimes,becauseaslongastheservergoesoffline,communicationbetweenuserswillbeimpossible.Thismeansthatthecentralserveristhekeytothesuccessorfailureoftheentirecommunicationandthefocusofattacks.Italsomeansthatitisalsothe"bottleneck"ofahugeorganization'scommunicationservices
Latest: Digital signal
Next: political system








