South Bridge Chip
Types
Intel
Since ICH2, Intel South Bridge chips have shown amazing strength, and each generation of North Bridge chips adopts brand new South Bridge chips. Match. ICH4 realized the support for USB 2.0 for the first time, and ICH5 introduced the SATA function. However, what is really worth our recollection is ICH6, which is also the embryonic form of the current Intel South Bridge chip.
Intel ICH6
Like ICH5, ICH6 is divided into two models: ICH6R and ICH6. The main difference between the two is the support of disk array functions. In addition to supporting common RAID 0 and RAID 1 disk array functions like ICH5R, ICH6R also adds a disk array mode called "Matrix RAID". The so-called Matrix RAID is more like a RAID 1.5 mode, which sacrifices 25% of the capacity to achieve the stability and data security of RAID 0+1. In terms of integration, ICH6 is also unprecedented. 4 Serial ATA channels, 1 parallel ATA interface, 4 PCI Express x1 expansion devices, integrated Gigabit network and 8 USB 2.0 interfaces, etc. In order to strengthen the Serial ATA function, Intel boldly discarded a parallel ATA interface, which means that users can only install one IDE hard disk and one IDE optical drive at most, unless an additional IDE control card is used.
The audio function is a highlight of ICH6. The Azalia controller integrated in the ICH6 South Bridge uses the new Azalia Link (AC'97 used AC-Link in the past) and many external Codecs ( Data signal conversion decoder) is connected, and the connection bandwidth is increased to a very high level. Only a single channel input bandwidth reaches 24MB/s, while the total bandwidth of AC-Link is only 11.5MB/s. In addition, Azalia Link supports multi-channel input and output, and manufacturers can use the corresponding mode according to their needs, up to 7.1 channels.
Intel ICH7 and ICH8
The ICH7 South Bridge chip has unprecedentedly derived a total of 5 versions, namely ICH7, ICH7DH, ICH7DO, ICH7DE and ICH7R, of which ICH7 is a standard type. ICH7DH is aimed at digital home entertainment computers, ICH7DO is aimed at commercial use, ICH7DE is aimed at computer gamers, and ICH7R is a version that supports RAID 0/1/5/1+0 disk array function.
In terms of integration, ICH7 is unprecedented. All ICH7 south bridges support 4 Serial ATA channels, which means that users will have more freedom when using Serial ATA serial hard drives, which lays the foundation for building a RAID disk array. More importantly, optical storage devices may also switch to Serial ATA interfaces in the future, so this improved design is necessary. ICH7's attitude towards parallel ATA interfaces also makes people feel more gratified. Instead of completely abandoning parallel ATA, it retains one parallel ATA interface, allowing users to connect two parallel ATA devices.
The new era of chipsets will focus on PCI Express. PCI Express is not a patent for high-performance graphics cards. It can even replace the existing PCI interface. The ICH7 standard version has 4 PCI Express Lanes, which means that it can provide up to 4 PCI Express x1 interfaces, while the other four enhanced versions provide 6 PCI Express Lanes, and even higher bandwidth PCI Express x4 interfaces are expected. When equipped with Gigabit network card, Ultra320 SCSI control card and other equipment, it will give play to certain advantages. ICH8 is an improved version of ICH7. In addition to the increase of USB ports from 8 to 10, SATA-II ports from 4 to 6, the first built-in Gigabit Ethernet controller, support for 6 PCI-E x1, start to support active management technology (iAMT) and In addition to the mute system technology, the biggest change is the comprehensive cancellation of the AC97 audio technology support, instead of retaining only the high-definition audio (HDA) output, and no longer providing the IDE interface for PATA, forcing the entry into the SATA era. ICH8 is divided into four different versions, namely low-end version ICH8, mainstream version ICH8-R, digital enterprise version ICH8-DO and digital home version ICH8-DH. Among them, ICH8R and ICH8-DH are paired with P965. The main difference is that the former supports the new version of Intel Matrix Storage Technology (MST). MST technology can provide two external 3Gbps eSATA interfaces, thereby increasing the number of SATA interfaces to 6, and supporting AHCI and RAID 0/1/5/10 modes.
Unique RAID mode
Matrix RAID disk array mode is a brand new RAID method introduced by Intel. In the past, most common ATA RAID controller chips were limited to RAID 0, RAID 1, or RAID 0+1. RAID 0 provides performance, and RAID 1 provides data security. To take into account both performance and safety, RAID 0+1 must be used, but this requires 4 hard drives and will waste half of the hard drive space. The Matrix RAID mode can create a RAID 0+1 environment using only two hard drives. Assuming there are two 80GB hard drives, we can form the first 40GB of the two hard drives into an 80GB logical partition, and then the remaining two 40GB blocks form a 40GB data backup partition. For applications that require high performance and do not require security, they can be installed on the RAID 0 partition, while data that requires security backup can be installed on the RAID 1 partition. In other words, the total hard disk space that users get is 120GB. Compared with traditional RAID 0+1, the efficiency of capacity usage is still very high, and there is a higher flexibility in capacity allocation.
iAMT technology is controversial
iAMT (Intel Active Management Technology) remote management technology was exposed as early as last year’s IDF Fall Forum, but it was thought that it would be integrated in Intel’s first Dual-core processor. However, Intel subsequently apparently changed its plan to transfer this technology to the ICH7 South Bridge chip, but only the ICH7 DO and DE versions support it. The standard version ICH7 and ICH7R and ICH7DE do not support iAMT technology for the time being.
In fact, iAMT technology was originally only used in the server field. It allows users to use new management functions to maintain their networked computers, even if the computer is not logged in or turned off. This set of technology can prevent users from deleting critical data, and provide remote remote control and anti-virus functions to provide a complete asset protection mechanism. You can check the software and hardware and update the BIOS remotely regardless of whether the machine is turned on or off. For enterprise users, this will greatly reduce MIS management costs. But not everyone welcomes this technology, because once the iAMT technology is popularized in all PCs, the authority of end users in the local area network will become smaller and smaller, and it will not even be able to manage local hard drives. In addition, iAMT technology is indeed a huge blow to those companies that specialize in system management software. The powerful technology of iAMT and the golden sign of Intel's industry leader will definitely attract a large number of enterprise users.
VIA
The chipset is VIA’s main business, and its market share is quite high. At the same time, it is involved in Intel and AMD platforms. It is precisely for these reasons that the development of VIA south bridge chips is quite fast, and reviewing the past generations of VIA south bridge chips is naturally a shortcut to fully understand the VIA chipset.
The most classic VT686B
VT686B is actually an upgraded version of VT686A, produced with a 0.35 micron process, working voltage is 3.3V, and 352-pin BGA package. VT686B is VIA's first highly integrated South Bridge chip, which adds support for AC97 and MC97, and integrates I/O controller and hardware monitoring functions. But more importantly, VT686B supports ATA100, which was also the most advanced external disk interface at the time, which completely solved the interface bottleneck. As a classic South Bridge chip, VT686B has created the brilliance of KT133A and 694X. The memorable VT686B South Bridge chip
Another major innovation of VT686B is its HDIT structural system standard. In terms of the number of pins, VT686B and 686A are exactly the same. The task of producing this chip can be completed on the original 686A production line, and the cost will not be much higher than that of 686A, which can guarantee its price advantage. It is one of the important reasons why it is widely supported by motherboard manufacturers. In addition, 686A and 686B allow manufacturers to decide whether to open all or part of their AC97 and MC97 functions according to their product positioning, which is more flexible. This design of VIA has continued to this day, so VT686B is indispensable.
VT823X series
The life span of VT8231 is not long, but it is the embryonic form of the VT823X series south bridge chip. After upgrading from VT686B to VT8231, this south bridge chip removes the I/O controller and hardware monitoring functions, so that the network card can be integrated. More importantly, the bandwidth of VT8231's V-Link technology with the Northbridge chip reached 266MB/s this time. In terms of output interface, VT8231 is still USB 1.1+ATA100, which is not much improved compared to VT686B.
VT8233 is another classic product. It has two upgraded products, VT8233A and VT8233C. They are generally matched with KT266A or P4X266A North Bridge chips. VT8233 is also the industry's first South Bridge chip to support ATA133 disk external interface, so it is also a milestone. It should be noted that the VT8233 South Bridge can be configured into two types: one is an 8-bit 266MB/s V-Link bus, and the other is a 16bit 533MB/s V-Link bus. In terms of port output capabilities, the VT8233 has advanced by leaps and bounds, supporting up to 6 USB ports and integrating a 10/100M network.
The epoch-making VT8233A south bridge chip
VT8235 is a more mature south bridge chip. Compared with VT8233, its biggest improvement is to support USB 2.0. In fact, VT8233C is already closer to VT8235 in terms of function. VT8235 also supports 16bit 533MB/s V-Link bus and ATA133. VT8237A is the last product in the VT823x series, and it appears as an improved version of VT8237. Most of the functions of VT8237A are the same as VT8337R, and HD Audio is added to provide high-quality audio output. In addition, two Serail ATA extension standards, Port Multiplier and Defer Spin up, have been introduced. The Port Multiplier standard allows 16 Serail ATA hard disks to be used in series, while the Defer Spin up standard allows multiple hard disks to slow down the compression speed when booting, preventing The hard disk was suddenly powered on and the system was damaged.
RAID5 and NCQ technology
RAID disk array technology is considered to be a good way to improve performance and increase data security. With the popularity of SATA hard disks, the feasibility of RAID on desktop platforms has become higher and higher. It is precisely because of this development trend that VIA has added RAID5 function to its VT8251 south bridge chip, which is also one of the few south bridge chips that can support RAID5. Compared with ordinary South Bridge chips that can only support RAID0 and RAID1, RAID5 is obviously geared towards higher-end applications, and it is also more practical than the so-called Matrix RAID.
Another major feature of VT8251 is that it supports SATA2 and includes NCQ technology. Although SATA2 increases the interface bandwidth to 3Gb/s, its actual performance improvement is minimal. In fact, the key that really determines the speed of the disk is the internal transfer rate. As long as the external transfer is higher than the internal transfer rate by about 30%, it is more than enough. The 3Gb/s transmission bandwidth provided by SATA2 is like a tap, and the actual internal transmission rate of current hard disks of about 60-70MB/s is like a cup. When the flow of the faucet obviously exceeds the capacity of the cup, increasing the flow again is almost meaningless and can only be a waste of effort.
What really makes SATA2 work is NCQ technology (helping the head to intelligently and efficiently seek). Only with the help of NCQ technology, SATA2 hard drives can truly show performance advantages. Unlike some South Bridge chips that partially support SATA2 but cannot support NCQ, VIA VT8251 fully supports SATA2 standards, and naturally also includes the valuable NCQ technology.
Other chips
SiS is steady and stable
As the traditional three major chipset manufacturers, SiS's South Bridge series still maintains the industry Leading position. The specifications of SiS 965 are very close to VIA's VT8251. The only difference seems to be that it does not support RAID5 disk array mode. The disk performance of the SiS South Bridge chip has been praised for a long time. Starting from the SiS 965 South Bridge, its South Bridge chip has 4 Serial ATA channels, which can be used in RAID0, RAID1 or RIAD0+1 mode, and is equipped with 2 parallel ATA channels, which is very expandable. What's more exciting is that SiS 965 to SiS 968 have built-in 8 USB 2.0 ports, as well as Gigabit network and 7.1 channel audio functions. In terms of North-South bridge connection technology, SiS has always had a great advantage. Multi-Threaded I/O Link technology helps SiS connect the North-South bridge with a real bandwidth of 1GB/s. The SiS 967 South Bridge released at the end of the third quarter of this year will even increase the Multi-Threaded I/O Link bandwidth to 2GB/s. This leads to better disk performance.
nVIDIA is pioneering and enterprising
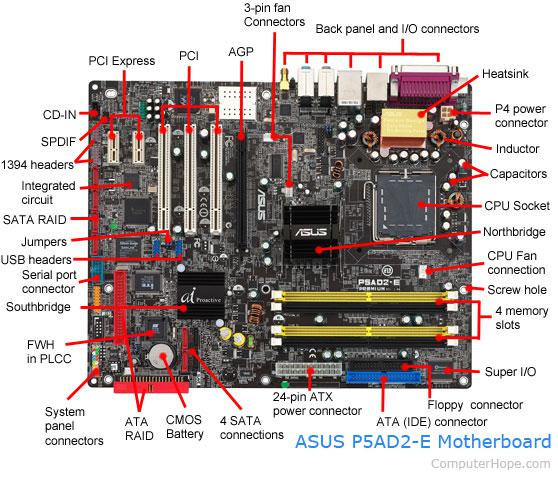
Although nVIDIA is not a traditional chipset manufacturer, with the outstanding performance of the nForce series, its position in the chipset industry has already Prospering day by day. However, what embarrassed nVIDIA is that the classic nForce2 has a perfect north bridge chip, but the performance of the south bridge chip is not flattering. Not only is the lack of Serial ATA functionality, but more importantly, there are USB controller compatibility issues. In order to change the passive situation, nVIDIA chose to remedy the situation by launching a variety of enhanced MCP2 south bridge chips on the nForce2 platform, which is also the basis of its later new south bridge. Among the many chipsets, the performance of the nVIDIA nForce 500 series stands out, which makes it a sought-after object for many consumers. In fact, nForce 500 does not have a strict South Bridge concept, but the part responsible for traditional South Bridge functions is very powerful, which is mainly reflected in network functions. Among the four nForce 500 products, except for the nForce 550, which is very general, the other three products all support dual Gigabit network cards, and FirstPacket technology shows extremely high usage. We know that in some delay-sensitive network software and games, when network resources are limited, it is easy to have related delay and conflict problems, and FirstPacket is to effectively solve this problem. It realizes the optimization of the actual application bandwidth of the software through the priority setting. Some software that is not sensitive to bandwidth can choose a lower priority, and let those sensitive software work at a higher priority to achieve reasonable and normal performance. Work. When we run online games or VoIP sessions at the same time, and turn on MSN software and Windows XP remote update, users can clearly experience the benefits.
In addition to this, nForce 500 also has TCP/IP acceleration technology. At this time, some tasks originally processed by the CPU can be directly completed in the chipset, which can reduce the impact on the CPU during heavy network transmission. Resource occupation. Of course, this technology of nForce 500 can also be implemented in many discrete graphics cards, but this is naturally commendable for integrated graphics cards. Even in terms of disk functions, the nForce 500 series has many advantages. Among them, supporting up to 6 SATA hard disks to form RAID5 is difficult for other South Bridge chips to reach.
Features
Dual-chip design
In addition to high-performance disk systems requiring high-speed hard disks and advanced disk controllers, they also require excellent north-south bridge connection bandwidth. For a long time, the bandwidth of the north-south bridge connection has been a very prominent problem. Since the bandwidth of the PCI bus was mostly occupied by IDE devices in the past, the communication speed between the north and south bridges cannot be guaranteed, which affects the performance of the system to a certain extent, especially when the IDE transmission tasks are heavy, such as in some entry-level situations. Level of servers and workstations. V-Link technology separates the North-South bridge communication from the busy PCI bus, which effectively guarantees the rapid and complete transmission of information within the chipset, which is of great help to the improvement of system performance.
After losing these advantages, the single chip naturally loses its fundamental existence value, and its drawbacks have gradually emerged. The first is the high heat generation of a single chip. Due to the substantial increase in integration, the heat generated by a single chip is often very strong. Take nVIDIA's nForce3 and nForce4 as examples. nVIDIA requires motherboard manufacturers to use high-quality heat sinks and strongly recommends active heat dissipation. This objectively increases costs and is not conducive to stability. Another very obvious feature is that the electrical performance of a single chip is slightly reduced, which affects the overclocking performance of the product. At the same time, the inherent low yield disadvantage of a single chip also affects chipset manufacturers. The chipset architecture of the North-South Bridge is getting more and more support, and its own starting point is to pursue stability and improve the yield rate, while also reducing costs.
The original purpose of using a single chip was to improve performance, because at this time the functions of the north and south bridge chips are completely integrated, and there is basically no problem of mutual communication. In addition, the single chip also reduces the size of the motherboard, making it easier to apply to special fields. However, with the development of north-south bridge connection technology, a single chip becomes increasingly unnecessary. Intel has a central acceleration structure, VIA has V-Link technology, and SiS has smart technology, and its connection bandwidth has reached the level of sufficient use. More importantly, ordinary PC motherboards can achieve mini size even with North-South bridge architecture.
Integrated network
Network function is undoubtedly the focus of the future development of South Bridge chips. Now that wireless network technology has been widely used, the integration of the South Bridge chip is the general trend. Starting from ICH6, Intel intends to integrate WiFi functions, while SiS and nVIDIA have had similar plans. Of course, the so-called integrated WiFi function of the South Bridge chip is only the physical layer, and the specific wireless signal transmission module still needs to be implemented by an external method. But what is certain is that once the South Bridge chip integrates WiFi functions, it will make WiFi technology thoroughly popularized. In addition to WiFi wireless networks, Wireless USB (Wireless USB) will also be the focus of the future development of South Bridge chips, but the relevant standards have not yet been fully formed.
Wireless network is one aspect, and wired network technology is also the focus of the South Bridge chip. In the past 25 years, as people's demand for higher and higher networking speeds continues to grow, Ethernet has also undergone many changes, from a half-duplex shared media 10Mbps LAN technology to a full-duplex 10/100 /1000/1000Mbps LAN switching technology. Intel's ICH10 South Bridge is ready to integrate 10Gbps network functions, which will help improve the existing LAN connection speed.
High-quality audio
The sound card can be regarded as the integration of the sound card control chip and the Codec chip, and the onboard sound card is no exception. Due to signal interference, the sound card control chip cannot be completely integrated in the South Bridge chip, but only the DSP chip. The specific digital-to-analog conversion and sound output and input have to rely on the Codec chip. The disadvantage of the integrated sound card is that the Codec chip is generally weak, and even if the more powerful DSP audio function is integrated in the South Bridge chip, the system resources it takes up are still not small. Our requirements for sound cards can be divided into two points: sound quality and sound effects. The sound effect part of the integrated sound card is completely dependent on the processing power of the DSP, and the sound quality has a great relationship with the Codec chip. From some technical indicators, we can often see that the integrated audio unit of a certain South Bridge can reach a very high level, but its role is very limited when it lacks API support.
However, the future South Bridge chip technology is eager to end this embarrassing situation. With the improvement of the manufacturing process level, it is not impossible to integrate the Codec chip in the South Bridge chip. More importantly, now chipset manufacturers are also beginning to pay attention to improving the performance of the sound card DSP. The current HD Audio is only a standard, and needs to be strengthened in terms of specific audio processing. In the nForce2 era of nVIDIA, we have already experienced SoundStorm as an example. Once the development goes well, nVIDIA also plans to launch SoundStorm2 in the future, and VIA plans to completely integrate the powerful Envy24.
Graphics card working bus
In the traditional architecture, the graphics card bus is completely in charge of the Northbridge chip. However, considering the future multi-display architecture and the possibility of gradually independent physical accelerator cards, the South Bridge chip provides the graphics card working bus has been gradually optimistic. In fact, ULi has made successful attempts in this regard. The M1567 South Bridge matched with the ULi M1695 North Bridge directly controls the AGP bus and is connected to the CPU through TGi technology. Now, a large number of South Bridge chips actually have PCI Express channels, so in the future, South Bridge chips will most likely have more PCI Express channels in the PCI Express 2.0 era, which will become more popular for multi-graphics applications. Summary: Through the above review and prospects, I believe that users have understood the role of the South Bridge. Although the roles of the South Bridge and the North Bridge are not comparable, and the attention is far less than that of the North Bridge, but understanding the South Bridge can still master the main board from the side. Development dynamics.
Function
The South Bridge chip is responsible for the communication between I/O buses, such as PCI bus, USB, LAN, ATA, SATA, audio controller, keyboard controller, real-time clock Controllers, advanced power management, etc., these technologies are relatively stable, so the South Bridge chip in different chipsets may be the same, but the North Bridge chip is different. Therefore, the number of north bridge chips in the motherboard chipset is far more than that of south bridge chips. For example, in the early Intel chipsets with different architectures, Socket 7's 430TX and Slot 1's 440LX all use 82317AB south bridge chips, while the Intel945 series chipsets in the past two years all use ICH7 or ICH7R south bridge chips, but they can also be matched with ICH6. South Bridge chip. What's more, the north-south bridges used in a few products produced by some motherboard manufacturers are products of different chipset companies. For example, in the previous Abit KG7-RAID motherboard, the north bridge used AMD 760, and the south bridge was VIA 686B.
The development direction of the South Bridge chip is mainly to integrate more functions, such as network cards, RAID, IEEE1394, and even Wi-Fi wireless networks. The South Bridge chip is the most important part of the motherboard chipset except the North Bridge chip. It is generally located on the motherboard far below the CPU slot and near the PCI slot. This layout takes into account its connection There are more I/O buses, and a little bit farther away from the processor is conducive to wiring, and it is easier to realize the wiring principle of equal length of signal lines. Compared with the north bridge chip, the data processing volume of the south bridge chip is not large, so the south bridge chip generally does not need to take active heat dissipation, and sometimes even the heat sink is not required.
However, different south bridge chips will have great differences in function, and manufacturers will choose matching according to cost control and market positioning. In fact, the development of the South Bridge chip can be described as very rugged. Starting from the chipset in the Pentium era, the prototype of the North-South bridge design architecture was initially established, which is also the beginning stage of the large-scale integration of motherboard functions. However, the subsequent "integrated single chip" trend made the South Bridge chip almost disappear, but it finally proved that the single chip design of the South Bridge is not a shortcut to control costs, and it is incompatible with the development trend of emphasizing the functionalization of the South Bridge.
Different south bridge chips can be matched with different north bridge chips. Although there is a certain corresponding relationship among them, as long as the connection bus matches and the pins are compatible, the motherboard manufacturer can choose at will. The most obvious example is the AMD-ATI chipset. Its north bridge chip can be used with its own south bridge chip or ULI or VIA south bridge chip. In addition, many typical chipsets can also use different south bridges. For example, in those days, Intel 845E could be used with ICH2 or ICH4. Even the ICH8 South Bridge, which is widely used in P965 motherboards, has differences in different versions, thus showing obvious functional differences.
Development history
As we all know, the predecessor of the AMD chipset is the ATI chipset. As early as 2006, after AMD officially acquired ATI, it began to market some ATI chipset products under the AMD brand, including CrossFire chipsets RD580, RD550 and RD480 for AMD platforms, and AMD launched after the acquisition of ATI Chipset products will no longer use the ATI brand, and only the graphics card will remain named after the ATI brand. It is worth noting that before the acquisition, ATI's motherboard chipset market share was not very high. After the acquisition, its market share of chipsets has been steadily increasing, such as the popular RS690G series chipsets before, and now they are very popular. The 7 series chipsets of the big fire are all products launched after mergers and acquisitions. Next, we will briefly review the past generations of ATI South Bridge chips with you.
ATI (the predecessor of AMD's chipset division) began to enter the South Bridge chip market in 2001. The first batch of chipset products listed on the market, ATi-S4/S5/S6, have specifications compared to similar products in the market. A lot behind: S4 supports AC97 sound effects, ATA66/S5 supports AC97, ATA100/S6 supports 3D sound effects, USB 2.0, built-in network card, etc....... The backward specifications of the South Bridge make ATI’s early chipsets have to adopt other companies’ South Bridge chipset, such as the M1575 of ULI ULI.
South Bridge Chip
The real rapid development of ATI South Bridge chipset started with the SB600. The main reason is that we will briefly explain it for you later.
First, let's take a look at the SB400, which is a milestone in the development history of ATI's south bridge chip.
SB400 will be connected to the North Bridge through two PCI-E buses, can support 8 USB 2.0 ports, 4 SATA 150 ports, can support serial hard drives, and also provide support for RAID 0,1 , 4 ATA-133 drives. In addition, SB400 can support 7 PCI expansion slots, with 5.1/7.1 channel AC'97 high-definition audio output capability. In addition, the SB400 does not have any highlight, it does not even integrate a network controller.
ATI claims that the integration of Gigabit network functions is not advantageous in terms of performance or cost compared with the Gigabit network functions implemented through the PCI Express bus. The RX480/RS480 chipset is the same as the Intel 925X. As long as the Gigabit LAN uses the PCI-Expree bus, what are the advantages of PCI Express? The biggest advantage is that it can reach 500MB/s transmission bandwidth, which is better in transmission efficiency. PCI needs to be faster and more efficient. The PCI Express Gigabit network function provides two-way 500MB/s total bandwidth for each device. Gigabit or 10/100 Ethernet can be supported by the PCI Express bus of the North Bridge or South Bridge, which allows manufacturers to provide high Performance or cheap network functions.
Next, let’s take a look at the SB450 South Bridge chip.
Compared with the predecessor SB400, the biggest improvement of SB450 is to upgrade AC97 equipment to Azalia codec, which is once again integrated with the current multimedia entertainment technology advocated by Intel. Azalia codec, also known as HD music, was originally developed by the Intel Developer Forum. It is expected to replace the old AC97 specification and provide a more flexible and cost-saving true high-level audio built-in solution. . The Azalia structure can transmit up to 8 channels of audio streams at 192KHz/32 bits; AC’97 can only support 6 channels at 48 KHz/20 bits. The increased bandwidth will bring users a trouble-free music experience when facing any discerning music function. In terms of storage, SB450 can provide 2 PATA channels and support 4 PATA devices. SB450 supports 2 SATA ports with a speed of 1.5GHz, but still cannot support SATA2. RAID supports the most commonly used modes 0 and 1.
SB450 supports 8 USB2.0 ports. The products tested in this test are all equipped with 4 USB2.0 ports, and the motherboard provides 4 USB2.0 external interface jumpers. Like the previous generation South Bridge chip SB400, it is a pity that SB450 does not have an integrated network card, so the motherboard must integrate a complete network card chip.
ATI SB600 can be said to be the most successful south bridge chip in the history of ATI south bridge development. This has a lot to do with competitor NVIDIA's acquisition of ATI south bridge chip partner ULI:
ATI Take a shortcut in the development of the chipset, first develop the north bridge chip and then slowly develop the south bridge. This leads to the general impression of the ATi chipset that the north bridge chip is good, especially in terms of graphics performance, but the south bridge is There are many problems and backward specifications, so it can only be used in low-end entry-level products. Products in the high-end mainstream market are entrusted to the ULi company at that time to design.
For many years, there has been a rumors in the motherboard industry that "to be a motherboard, do the South Bridge first." The end of NVIDIA’s acquisition of ULi began to appear
. After NVIDIA completed the acquisition of ULi internally, it began to cut off the supply of ATi’s south bridge. For a time, ATi’s high-end RD580, RD480 and other north bridge chips became isolated. Bird, there is no corresponding South Bridge to match. SB600 South Bridge is a high-specification South Bridge independently designed by ATi to replace ULi M1575. It can be said to be a product of NVIDIA's acquisition of ULI. Compared with previous ATi products, the biggest improvement of SB600 lies in the disk performance. The most criticized on the SB400 South Bridge is the USB performance. The SB450 adds HDA sound effects on the basis of correcting some bugs in the SB400. The disk performance is still maintained at 1.5 of the SB400. Gbps SATA x 4. Therefore, SB600 has improved the performance of the disk and added the AHCI interface, so that the NCQ technology hard disk using this interface can be supported. In addition, the transmission rate of the SATA interface has been increased from the original 1.5Gbps to 3.0Gbps, and RAID 0, 1, 10 is supported. IDE is reduced to 1 Channel, and the number of USB ports is increased to 10.
3. Comparison of SB600/SB700 South Bridge specifications between the new and old generations
Before the SB600 was launched, AMD’s deficiencies in the South Bridge were known to everyone. Because of these deficiencies, AMD was not allowed to Do not use the third-party south bridge solution provided by ULi, and after NVIDIA acquired ULi in one fell swoop, AMD’s lack of a south bridge has become more prominent, and it was not until the launch of SB600 that the SB450/SB460’s low USB performance, such as poor performance, was really solved. The user feels a headache.
As storage technology gains new applications and increases system security requirements, SB600 is bound to be replaced by newer products. So SB700 continues the many advantages of SB600 and comes to us. Compare SB600 And SB700 specifications, you can see a lot of improvement. First of all, the number of supported expansion interfaces has been further increased. The original 10 USB 2.0 interfaces have now reached 12 USB 2.0 and 2 USB 1.1 interfaces. The original 4 SATA II interfaces have now been added to 6 at the same time. Support RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1, RAID 10, JBOD, and support eSATA.
There is also support for the Trusted Platform Module (TPM). "Trusted Platform Module (TPM)" is a trusted security platform module. Through the "TPM" module integrated on the motherboard, the user’s personal The computer can be very securely protected. The TPM solution is based on the physical layer, combined with a universal authentication type identity management strategy. Its advent means that a complex, difficult to remember and easy to crack user password method is about to be launched in the historical stage. TPM is very common in notebooks and some branded desktop computers. And we know that SB700 is also designed to be used on the south bridge of the notebook platform, so this design is very popular with notebook users.
But the biggest improvement is that it can support HyperFlash technology. We know that Microsoft
The new generation of operating system Vista has added ReadyBoost and ReadyDrive technology, which improves the operating system through additional storage particles. As well as the efficiency of application startup, Intel has added the new Turbo Memory technology to the new generation of Centrino platform Santa Rosa released a long time ago. It is logical for AMD to add the new HyperFlash technology in this generation. This technology will adopt Samsung. The OneNAND Flash module reduces the volume and effectively reduces the cost. The ReadyBoost and ReadyDrive functions of the new-generation Windows Vista operating system can shorten the startup time of the operating system and applications, provide a larger cache capacity for the hard disk, increase the read and write time, and reduce the number of hard disk startups and rotations, and reduce the power consumption of the hard disk. , To further improve battery life (it seems that SB700 was born for notebook platforms), and Intel Turbo Memory technology supports the above two functions, allowing better performance when operating Vista.
AMD's new HyperFlash technology added to the SB700 South Bridge will integrate the flash memory controller circuit with the IDE bus, support Samsung OneNAND chips, up to 4 chips, the chip frequency is 80MHz, and the 16Bit interface has the highest transmission The speed is 108MB/s, and it is claimed to be 30% faster than Intel Turbo Memory.
Currently, the module used by HyperFlash is designed by Molex. PC manufacturers can produce HyperFlash cards by themselves, which can support 512MB, 1GB and 2GB capacities. Compared with Intel Turbo Memory, which must be produced by Intel itself, HyperFlash is attractive Naturally higher, if the HyperFlash marketing strategy succeeds, it will be expected to force Intel to decentralize Turbo Memory production to PC manufacturers.
Summary:
The chipset is the soul of a motherboard. The functions, performance and technical characteristics of a motherboard are determined by the characteristics of the motherboard chipset. All along, the chipset has always been based on the north bridge as the main chip and the south bridge as the auxiliary chip. Because the north bridge is responsible for connecting to the CPU, memory, and graphics card, the chipset with integrated display functions also integrates the display core in the north bridge; while the south bridge chip is only responsible for peripheral devices. Through this article, I believe that everyone has a general knowledge and understanding of the AMD platform South Bridge chipset.
Latest: Von Neumann System
Next: RDRAM memory







