Simple network management protocol
Introduction
SNMP is specifically designed to be a standard protocol for IP network management network nodes (servers, workstations, routers, switches and HUBS, etc.), which is an application layer protocol. SNMP enables network administrators to manage network performance, discover and resolve network issues, and planning network growth. The network management system has a problem with the network management system by SNMP Receiving Random Message (and Event Report).
SNMP is a Simple Gateway Monitoring Protocol (SGMP) to manage communication lines. Subsequently, people have made great modifications to SGMP, especially the SMI and MIB-defined SMI and MIBs, and the improved protocol is the famous SNMP. The SNMP network management framework based on TCP / IP is an industrial current standard. It consists of three main part, which is the management information structure SMI (Structure OFManagement Information), manage the information library MIB and management protocol SNMP.
-
SMI defines the organization and identity of the information used by the SNMP framework, and provides templates for the MIB definition management object and use the management object.
-
MIB defines a collection of management objects that can be accessed by SNMP.
-
SNMP protocol is an application layer protocol that defines how network managers perform read and write operations for the MIB object of the proxy process.
SNMP is a tree database, MIB-managed object, is the end node of the tree, each node has a unique location and unique name .ietf Managing the Library Object Idifier (OID, Object Identifier) Uniquely specified, its naming rules are the name of the parent node as the prefix of the child node name.
Component
Networks of SNMP management consists of the following three key components:
-
network management system (NMS, network- Management systems
-
Managed device
-
agent (Agent)
Network management system runs the application, monitors and controls the managed devices with this application. Also known as managed entities, network administrators interact with network devices here. The network management system provides a large number of computational and memory resources required for network management. A managed network may have more than one network management system.
Managed devices is a network node that contains a SNMP agent that exists in the managed network. Managed devices collect and store management information through the management information library (MIB), and allow the network management system to get this information through the SNMP agent.
The agent is a network management software module existing in the managed device. The agent controls the management information of the local machine to transmit this information with SNMP-compatible format.
Technical Advantages
SNMP is a communication protocol between management process (NMS) and agent process (Agent). It specifies the standardized management framework for monitoring and management in the network environment, the public language, corresponding security and access control mechanisms of communications. The network administrator uses the SNMP function to query device information, modify the parameter value of the device, monitor the device status, automatically discover network fault, generate reports, etc.
SNMP has the following technical advantages:
-
Based on TCP / IP Internet standard protocol, the transport layer protocol generally uses UDP.
-
automation network management. Network administrators can use the SNMP platform to retrieve information, modify information, discovery, fault, complete trouble diagnosis, and generate reports.
-
Shielding the physical differences of different devices, realizing automation management of different manufacturers products. SNMP only provides the most basic set of functional sets, enabling management tasks and physical features and actual network types of managed devices to implement management of different manufacturers.
-
Simple request - a combination of response and active advertisement methods, and has timeout and retransmission mechanisms.
-
The type of packet is small, the message format is simple, easy to resolve, easy to implement.
-
SNMPv3 version provides authentication and encryption security mechanism, as well as user and view access control functions, enhances security.
architecture
Main agent
The main agent is a software operated on network components that can run SNMP, Responding to SNMP requirements from the management station. Its role is similar to the server in the client / server structure (Client / Server) term. The primary agent relying on the child agent provides management information about a particular function.
If the system currently has a plurality of manageable subsystems, the primary agent will pass it from one or more sub-agent received. These sub-proxy models in an interface of monitoring and managing the operation of that subsystem. The role of the primary agent and sub-agent can be merged, in which case we can simply call it a proxy (agent).
sub-agent
sub-agent is a software operated on a network component that can run SNMP, run in a specific management information library of a specific subsystem (MIB, Management Information Base) Defined information and management functions. Some capabilities of child agents are:
Information of the primary agent
Configuring the main agent's parameter
Response Manager's requirements
Producing warnings or traps
The good separation of protocols and management information structures makes it very simple to monitor and manage different subsystems in the same network in the same network. The MIB model runs all layers of the management OSI reference model and can extend to applications such as databases, email, and J2EE reference models.
management station
administrator or management station provides a third component. It works like a client under the client / server structure. It issues a request for a management operation based on a manager of an administrator or application, and also receives the TRAP obtained from the agent.
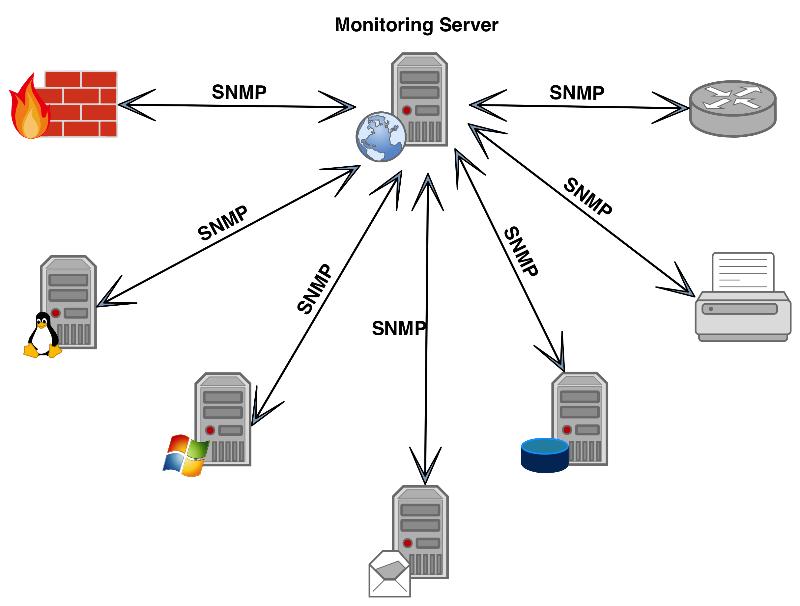
Agreement type
Currently, SNMP has three types: SNMPv1, SNMPv2, SNMPv3. The first and second editions do not have much gap, but SNMPv2 is an enhancement version that contains other protocol operations. Compared to the first two, SNMPv3 contains more security and remote configurations. In order to solve the incompatible problems between different SNMP versions, the RFC3584 defines three coexistence strategies.
SNMP also includes a set of extended protocols defined by RMON, RMON2, MTB, MTB2, OCDS, and OCDS.
protocol structure
SNMP is an application protocol, encapsulated in UDP. Various versions of the SNMP information universal format as follows:
Version Community PDU
Version: SNMP version number. Manager and proxy must use the same version of SNMP. Information with different version numbers is required and do not process them.
Community: Group name for authentication manager before accessing the Agent.
PDU (Protocol Data Unit): The PDU type and format in SNMPv1, V2, and V3 will be specifically described in the corresponding file.
Development and use
1st version
SNMP first RFC series is currently 1988:
RFC 1065: Based on The structure and identification of the management information of the TCP / IP network
RFC 1066: Management information based on network management based on TCP / IP network
RFC 1067: a simple network management protocol
These protocols are abolished via:
RFC 1155: the structure and identification of management information based on TCP / IP network
RFC 1156: based on TCP / IP Network management-based management information
RFC 1157: A simple network management protocol
SNMP protocol works in an OSI model (seventh layer). It (in the first edition) specified four core protocol data units (PDUs):
get, used to get a management information
getNext, used to repeatedly get management information Serial
set, is used to create a change
trap for a managed subsystem to report a warning or other asynchronous event for managed subsystems
typically, SNMP uses UDP port 161 for the agent to use UDP port 162 for the management station.
The first version is controversial because of its fragile security. The client's authentication uses the coded transmission. In the 1980s, the SNMP first edition was designed, and the Internet standard certification / security was not valued by the main agreement design group.
Second Edition
SNMP Second Edition (RFC 1441-RFC 1452) revised the first version and included communication between performance, security, confidentiality, and managers Improvement in the field. It introduces GetBulk to replace the repeated GetNext to get a lot of management data in a single request. However, SNMP second edition new security system is considered too complicated without being widely accepted.
SNMP V2C (community-based SNMP Second Edition) is defined in RFC 1901-RFC 1908, which is also informally referred to as SNMP version 1.5. The SNMPv2C includes SNMP second edition except for parties other than the disputed SNMP second edition security model, and the Simple community-based security scheme of SNMP is taken.
SNMP V2U (SNMP Based on User) is defined in RFC 1909-RFC 1910. This is a compromise program for SNMP first edition and SNMP second edition, trying to provide better security than SNMP first edition, and does not encounter the high complexity of SNMP second edition. This produces an commercial variant called SNMP V2 *, and its mechanism is finally employed by one of the two security frames of SNMP.
Third Edition
Internet Engineering Working Group (IETF) puts the SNMP third edition defined in RFC3411-RFC3418 (STD0062) as a standard version of 2004. IETF will set the previous version to "Obsolete" or "Historical".
In fact, SNMP implementations typically support multiple versions: typical SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. See the RFC3584 "Internet Standard Network Management Framework, the coexistence of the second, third".
SNMP third edition provides three important services: authentication, privacy, and access control.
Application
In large network management, the problem with the network administrator's headache is how to understand the health of network devices that are not around. If you want to go to see the operation status of the network device, it is not very realistic. In the actual network, the application is the most widely used by the SNMP protocol to automatically help administrators collect network health. In this way, network administrators only need to sit in their own position, you can understand the operation of the company's network equipment. With this simple network management protocol (SNMP), the network administrator can easily exchange management information between SNMP Agent and NMS. The main role of SNMP is to help enterprise network managers make more convenient to understand network performance, discover and solve network problems, and plan the future development of the network.
Latest: High-level atmospheric physics
Next: Network architecture







