Numerical aperture
concept
Numerical aperture is the main technical parameters of lens and concentrating mirrors, is judged (particularly on objective glasses) performance (ie, the ability of the elimination of the color difference, the value of Zeiss Company) The aperture is an important symbol of the ability to deplete the color difference and the multivision color difference. The size of the value is labeled on the outer casing of the objective lens and the concentrating mirror, respectively.
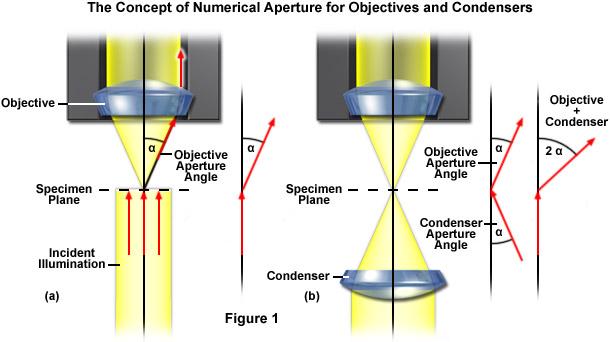
Numerical aperture (NA) is a larger induced (N) and aperture of the diameter (2α) of the lens and the subject body. The following formula is as follows: Na = n * sin α. The aperture angle is also known as the "mirror angle", is an angle formed by the object point on the optical axis of the lens and the effective diameter of the objective front lens. The larger the aperture angle, the larger the luminous flux into the lens, and it is proportional to the effective diameter of the lens, which is inversely proportional to the distance of the focus.
Here, it must be noted that in order to sufficiently exert the effect of the value of the objective hole diameter, the Na value of the concentrating mirror should be equal to or slightly larger than the NA value of the objective lens.
numerical aperture reflects the coupling efficiency between the fiber and the light source. There is an air gap between the light source and the optical fiber end face, and only a portion of the light incident on the end surface can enter the optical fiber, and the light enters the optical fiber end face can only partially meet the specific conditions, and propagate in the fiber. As can be seen from the figure, only the rays that are incident than Q0 from Q0 from the air gap to the optical fiber end surface can be propagated. Q0 is actually a spatial angle, that is, if light is incident on the end surface of the tapered region limiting 2Q0, the light can be captured by the fiber. The larger the QO, the smaller the difference between the refractive index of the core and the cladding, the stronger the ability of the fiber to capture the light, and the parameter sinqo directly reflects this capability, which we call the value of the fiber. NAF NA.
Technical parameters
Numerical aperture has a close relationship with other technical parameters, which decides and affects other technical parameters. It is proportional to the resolution, which is proportional to the magnification, the square of the focus depth and the numerical aperture, the NA value is increased, and the field width and the working distance will become smaller accordingly.
Laser Physics
In the field of laser physical field, the definition of numerical aperture is slightly different. The laser beam is diverged in the process of occurrence. Where the narrowest point away from the light beam is, the degree of divergence of the beam is substantially linear - equivalent to the beam in "far field" forming a cone. In this case, the definition of the numerical aperture is still:
where λ0 is in vacuum The wavelength, 2W0 is a beam diameter (equivalent to the full width of the irradiance attenuated to 1 / E). This means that the laser on the small buckle spots will be spread very quickly, and the laser having a large diameter diameter can remain almost constant in a long propagation distance.
Optical fiber optics
In multi-mode optical fibers, only light along a particular cone angle (that is, so-called receiving cone angle) into the optical fiber can be propagated along the optical fiber. The half angle of the cone angle is referred to as being protruding angle θmax. For mutant multimode fibers, the size of the optic angle depends only on the refractive index of the optical fiber core and the external cladding layer:
Increase Numerical Way
In the microscope system, for a given objective lens, the aperture angle has been fixed, if it is intended to increase its NA value, the only way is to increase media refraction Rate n value. Based on this principle, a water immersion objective lens and an oil immersion mirror are generated.
Because the refractive index n value of the medium is greater than 1, the NA value may be greater than 1. If the refractive index is high, the refractive index of the naphthalene is 1.66, then the NA value can be greater than 1.4.
Object resolution
| objective type | |||||||||||||||||
| Pieces of color difference | flat field fluorite Field resin color difference lens | ||||||||||||||||
| < P> 放 放 | Na | Resolution (micrometer) | < P> Na <104> resolution (micron | Na | Resolution (micron) | 4 times | 0.10 | 2.75 | 2.12 | 0.20 | 1.375 | 10 times | 0.25 | 1.10 | 0.92 | 0.45 | 0.61 |
| 20 times | 0.40 < / TD> | 0.69 "69> 0.50 < / p> | 0.55 | 0.75 < / b> | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.37 | 0.95 < / TD> | 0.29 | ||||||||
| 60x | 0.75 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.95 | 1.25 | 0.21 | 1.4 0 |
Latest: Angel's Knock
Next: Big Data System Software Country Engineering Laboratory







