megahertz
Introduction
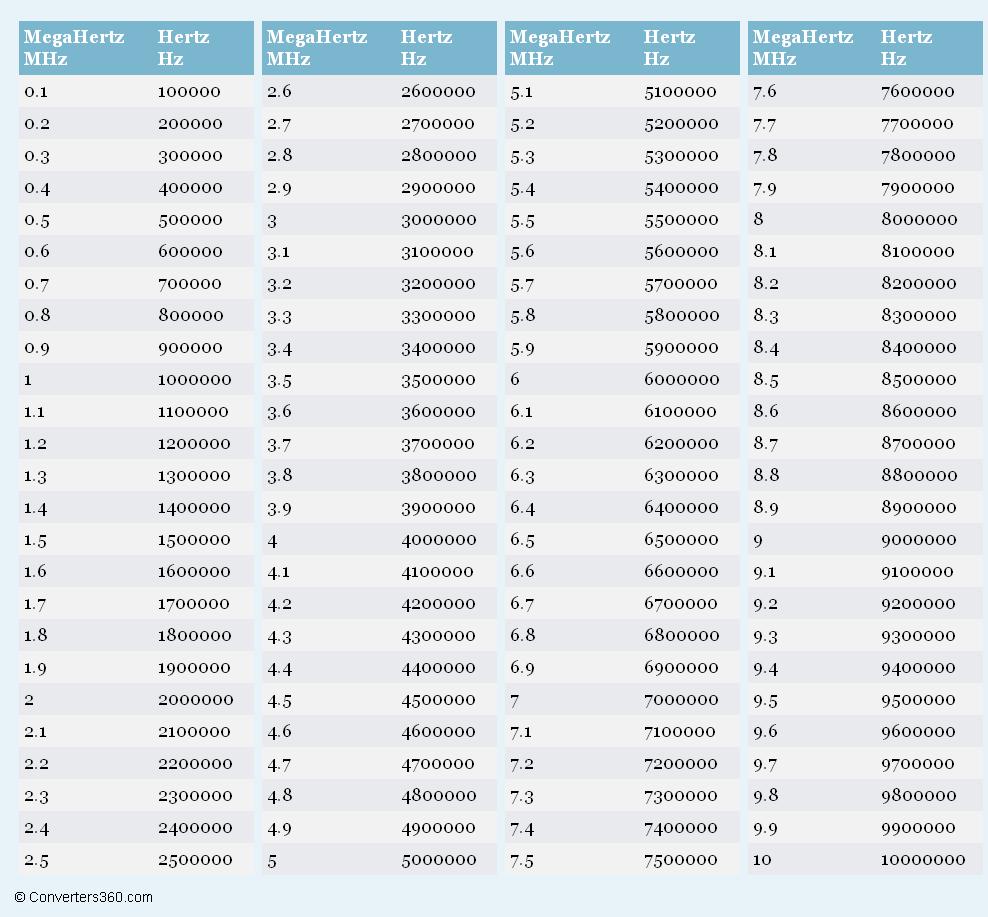
ThebasicunitoffluctuatingfrequencyisHertz,whichisbasedonthethousand-carryingsystem;1MHzisequivalentto1000kilohertz(KHz),whichis10tothe6thpowerofHz.Itisworthnotingthatmegahertzisjustadefinitionalnoun,with1millionsolutionsinthemeasurementunit.
IntheradiofrequencydivisiondefinedbytheInternationalTelecommunicationUnion:
Verylowfrequency(VLF):3~30kilohertz(KHz)
Lowfrequency(LF):30~300kilohertz(KHz)
Intermediatefrequency(MF):300~3000kilohertz(KHz)
Highfrequency(HF):3~30MHz(MHz)
VHF:30~300MHz(MHz)
UHF:300~3000MHz(MHz)
p>Ultrahighfrequency(SHF):3~30gigahertz(GHz)
Extremehighfrequency(EHF):30~300gigahertz(GHz)
unitConversion
ThebasicunitoffrequencyisHertz(Hz),abbreviatedasHertz,1Hz=1/s,thatis,thenumberofvibrationscompletedperunittime.
1kilohertz(kHz103Hz)=1000Hz
1megahertz(MHz106Hz)=1000000Hz
1gigahertz(GHz109Hz)=1000000000Hz
1terahertz(THz1012Hz)=1000000000000Hz
1beathertz(PHz1015Hz)=1000000000000000Hz
1EHz(EHz1018Hz)=1000000000000000000Hz
Relatedconcepts
Hertz
HertzisalsoaunitoffrequencyintheInternationalSystemofUnits.Itisameasurementofthenumberofrepetitionsofperiodicchangesinaunitoftime.Hertz'snamecomesfromtheGermanphysicistHeinrichRudolfHertz.ThesymbolisHz.
1Hz=1/s,thatis,thenumberofvibrationscompletedinaunittime,theunitisHertz(1Hz=1time/second).
Frequency
Frequencyisthenumberofcyclicalchangescompletedinaunittime,andisaquantitydescribingthefrequencyofperiodicmotion.Commonlyusedsymbolsforνmeans,theunitisonepartofasecond,andthesymboliss-1.InordertocommemoratethecontributionoftheGermanphysicistHertz,peoplenamedtheunitoffrequencyHertz,abbreviatedas"Hertz",andthesymbolisHz.Everyobjecthasafrequencythatisdeterminedbyitsnatureandhasnothingtodowiththeamplitude,calledthenaturalfrequency.Theconceptoffrequencyisnotonlyappliedinmechanics,butalsooftenusedinelectromagnetics,opticsandradiotechnology.
Latest: Public telephone
Next: Surface roughness







