imap
Definition
IMAP and POP3 (POST Office Protocol - Version 3, post office protocol third edition) is the most common Internet standard protocol for mail access. In fact, all modern mail clients and servers are supported by both. The IMAP version is "IMAP Fourth Edition First Revision" (IMAP4REV1), defined in RFC 3501.
IMAP is designed by Mark CRISPIN, providing another choice for a widely used POP3 mail protocol for mail access. Basically, both allow a mail client to access information stored on the mail server. Some important aspects only in IMAP include:
-
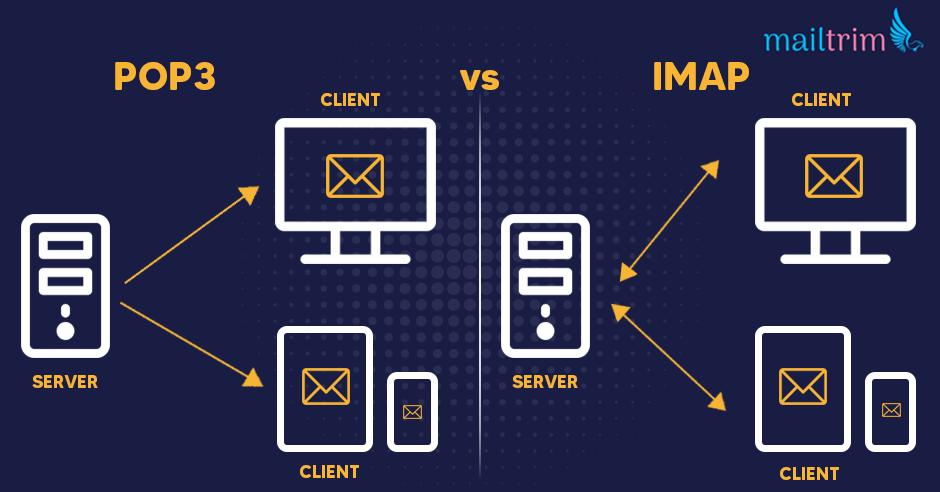
supports connection and disconnecting two mode of operation. When using POP3, the client will only connect to the server for a while until it is downloaded all new information, and the client is disconnected. In IMAP, the client will always connect the server as long as the user interface is active and the download information content is required. For users with a lot of or large mail, use IMAP4 mode to get a faster response time.
-
supports multiple customers to connect to a mailbox. The POP3 protocol assumes that the current connection of the mailbox is a unique connection. In contrast, the IMAP4 protocol allows multiple users to access mailbox simultaneously and provide a mechanism to make customers feel that other users currently connect to the user's mailbox.
-
supports the MIME section and part of the access message. Almost all Internet messages are transmitted in MIME format. MIME allows messages containing a tree structure, and the leaf node of this tree structure is a single content type rather than a combination of multiple types of types. The IMAP4 protocol allows the client to get any independent MIME section and some or all of the information. These mechanisms allow users to browse the message content without downloading attachments or browsing while obtaining content.
-
supports the server to reserve message status information. By using the flag client defined in the IMAP4 protocol, you can track the message state, such as whether the message is read, reply, or delete. These identities are stored in the server, so many customers can perceive the operations made by other users at different times.
-
supports accessing multiple mailboxes on the server. The IMAP4 client can create, rename, or delete a mailbox on the server (usually manipulating to the user in folder). Support multiple mailbox also allows the server to provide access to shared and public folders.
-
supports server-side search. IMAP4 provides a mechanism to enable customers to request server search to match multiple standard information. Under this mechanism, the client does not need to download all the information in the mailbox to complete these search.
-
supports a well-defined expansion mechanism. The experience of extracting the early Internet protocols, the Imap extension defines a clear mechanism. Many extensions for the original protocol have been proposed and widely used. Regardless of the use of POP3 or IMAP4 to get the message, the client uses the SMTP protocol to send messages. The mail client may be a POP client or an IMAP client, but it will use SMTP.
Directory service for most mail programs also uses LDAP.
Not like most old Internet protocols, iMap4 supports encryption registration mechanism. It also supports the express delivery password in IMAP4. Because the use of encryption mechanisms requires the consistency of both clients and servers, the use of plain text passwords are different in some clients and server types (such as Microsoft Windows clients and non-Windows servers). The use of SSL can also encrypt the communication of IMAP4, and "StartTLS" is declared by transmitting the IMAP4 communication in SSL through the 993 port or when it is created in the IMAP4 thread.
IMAP4 uses port 143 to work on TCP / IP connection.
Features
Similar to the POP3 protocol, the IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is also providing a user-oriented mail collection service. Common versions are IMAP4.
IMAP4 improves the shortcomings of POP3, and users can decide whether to collect, delete and retrieve mail, or change folders or mailboxes on the server by browsing, deleting and retrieving specific parts of mail. In addition to supporting the offline operation mode of the POP3 protocol, it also supports online operations and disconnect operations. It provides users with a selection of selections that receive mail from the mail server, based on the server's information processing function and shared mailbox feature. The offline mode of the IMAP4 is different from POP3. It does not automatically delete the email that has been taken on the mail server, and its online mode and disconnect mode are also accessing the mail server as the "Remote File Server", more flexible and convenient. IMAP4 supports multiple mailboxes. These features of
iMap4 are ideal for users who operate mail between different computers or terminals (for example, you can operate the same email address on mobile phone, pad, and pc), and those use Multiple mailbox users.
Function
supports connection and disconnecting two mode of operation. When using POP3, the client will only be connected to the server for a period until it is downloaded all new information, and the client is disconnected. In IMAP, as long as the user interface is active and the download information content is needed, the client will always be connected to the server. For users with a lot of or large mail, use IMAP4 mode to get a faster response time. Support multiple customers to connect to a mailbox. The POP3 protocol assumes that the current connection of the mailbox is a unique connection. In contrast, the IMAP4 protocol allows multiple users to access mailbox simultaneously and provide a mechanism to make customers feel that other users currently connect to the user's mailbox. Support the MIME section and part of the access message. Almost all Internet messages are transmitted in MIME format. MIME allows messages containing a tree structure, and the leaf node of this tree structure is a single content type rather than a combination of multiple types of types. The IMAP4 protocol allows the client to get any independent MIME section and some or all of the information. These mechanisms allow users to browse the message content without downloading attachments or browsing while obtaining content. Support in the server to reserve message status information. By using the flag client defined in the IMAP4 protocol, you can track the message state, such as whether the message is read, reply, or delete. These identities are stored in the server, so many customers can perceive the operations made by other users at different times. Support to access multiple mailboxes on the server. The IMAP4 client can create, rename, or delete a mailbox on the server (usually manipulating to the user in folder). Support multiple mailbox also allows the server to provide access to shared and public folders. Support server-side search. IMAP4 provides a mechanism to enable customers to ask the server to search for information on multiple standards. Under this mechanism, the client does not need to download all the information in the mailbox to complete these search. Support a well-defined expansion mechanism. The experience of extracting the early Internet protocols, the Imap extension defines a clear mechanism. Many extensions for the original protocol have been proposed and widely used. Whether you use POP3 or IMAP4 to get a message, the client uses the SMTP protocol to send. Mail customers may be a POP client or an IMAP client, but all use SMTP.
Typical application
Factory range engineering and configuration In modular machine / factory, there must be a cross-plant configuration tool to define stand-alone / factory components or machines. The relationship between units. SIMATICIMAP is a component-based software tool. It is used to configure communication with a distributed automation scheme. SIMATICIMAP is used to granly data exchange between configuration technology function templates. In order to ensure data exchange between intelligent field devices from different suppliers, SIMATICIMAP is also based on PROFINET, PROFIBUSINTERNATIONAL (PNO) standard communication protocol. PROFINET defines communications based on TCPIP and Industrial Ethernet from different manufacturers. SIMATICIMAP can be integrated into an existing solution as an upper configuration tool, such as a total integrated automation system. In this case, STEP7 generates a library component.
SIMATICIMAP is a Windows-based application for configuring communication between the technical function template (PROFINET equipment) in the machine / factory. SIMATICIMAP basically includes the following basic views:
. Project tree: used to manage all project resources (technical functions and devices) and navigation for automation levels of the factory.
· Technology Ribbon: Technical Function The technology software features needed for a project. Technical ribbon components must be provided by OEMs.
• Link Editor: Data exchange between the technical function template.
• Network and topology view: Used to define technical functional structures between hardware devices, and system diagnostics (communication and device status diagnostics)
· project view: for project management And the software function overview in the project.
Program compared to the communication function in the user program of each single device, the main advantages of SIMATICIMAP is simple (only the line between the technical function interface of the device).
Latest: Hunan Science and Technology Press
Next: Strive for socialism








