Hardware virtualization
Introduction
Virtualization In 1960, this concept was first proposed in order to describe the virtual machine (experimental IBMM44 / 44X system). Eating and management of virtual machines is called platform virtualization, and now also known as server virtualization.
Platform Virtualization is performed to create an analog computer environment (virtual machine) to the client in a given hardware platform. Client software has no restrictions on user applications; many hosts allow running real operating systems. The client seems to be running directly on computer hardware, accompanied by several obvious warnings. Virtual Machines Access to hardware resources (such as networks, monitors, keyboards, hard disks) is managed at a more restricted level than processor and system memory. Customer software is often restricted access to computer peripherals, or is limited to lower device performance, depending on the host hardware access policy setting.
Virtualization Cause
In the computer cluster, many small servers are replacing a large server to increase the utilization of hardware resources (such as CPU, etc.). Although hardware is being integrated, a typical operating system is still independent. Instead, each operating system running on a stand-alone server is transferred to in the virtual machine. Large servers can "host" many "customer" virtual machines. This is the conversion of Physical-to-Virtual, P2V).
The virtual machine can be more easily controlled and checked from the outside, and can be configured more flexible. This is especially useful in kernel development and operating system curriculum teaching.
Creating a new virtual machine does not need to purchase hardware in advance. At the same time, a new virtual machine can easily transfer from one computer to another. For example, a salesman can copy a virtual machine containing the trial software to his laptop to access his customers without replacing the computer. Similarly, the failure in the virtual machine will not cause damage to the host, so it will not let the operating system on the notebook crash.
Since it can be easily migrated, the virtual machine can be used for a long disaster recovery scheme.
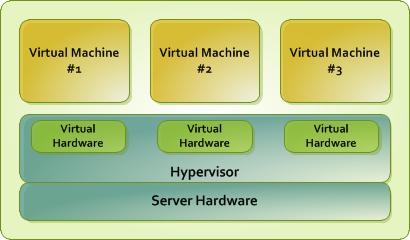
Platform virtualized solutions have a lot.
Full virtualization
In full virtualization (Fullvirtualization), the virtual machine simulates a strong hardware to operate independently of the client operating system. This solution was used in the Pioneer IBMCP-40 with the virtual machine family in 1966 and CP-67. Support for fully virtualized virtual machine software includes ParallelsWorkstation, ParallelsDesktopforMac, VirtualBox, VirtualIron, OracleVM, VirtualPC, VirtualServer, Hyper-V, VMwareWorkstation, VMwareServer (formerlyGSXServer), QEMU, Adeos, Mac-on-Linux, Win4BSD, Win4LinPro, and EgeneravBladetechnology .
Hardware Assistive Virtualization
In Hardware-AssistedVirtualization, hardware Provide Structure Support Helps to create virtual machine monitoring and allow client operating systems to run independently. Hardware assisted virtualization In 1972, in order to use the first virtual machine operating system VM / 370, the first time is introduced by IBMSystem / 370. In 2005 with 2006, Intel and AMD provided additional hardware support for virtualization. Support for hardware-assisted virtualization with Linuxkvm, VMwareworkStation, VMwareFusion, MicrosoftVirtualPC, Xen, ParallelsDesktopFormac, VirtualBoxandParallelSworkstation.
Support for complete virtualization technology, hardware platforms include:
x86 (andx86_64) -AMD-V (Code Pacifica), IntelVt (Code Vanderpool)
The IOMMU is developed by AMD and Intel.
PowerArchitecture (IBM / Power.org)
Virtage (Hitachi)
Ultrasparct1, T2 and T2 + (Sun)
part of virtual
In partialvirtualization (including address space virtualization), virtual machine simulation (but not all) underlying hardware environments, especially address space. Such environment supports resource sharing and thread independence, but the independent client operating system is not allowed. Although this is not considered a virtual machine in the general sense, this is a very important page in history. This technology has been used for CTSS (experimental IBMM44 / 44X), as well as controversial systems such as MVS and Commodore64 (both are "Taskswitch" programs).
Parallel Virtualization
In parallel virtualization (Paravirtualization), the virtual machine does not need to simulate hardware, but provides a special API that can only be used by a special client operating system. .
Operating system layer virtualization
In OS-LevelVirtualization, the standalone host is virtualized in the operating system layer, which makes multiple independent and safe Virtualized servers run on a computer. The customer operating system environment shares the same operating system with the host server, for example, the same system kernel is used to create a client environment. The program is run in a client environment that is considered a standalone system. This approach is created by FreeBSDjails; similar examples include Solariscontainers, OpenVZ, Linux-Vserver, AixWorkloadPartitions, Parallelsvirtuozzocontainers, and IcoreVirtualAccounts.
Latest: Augusta
Next: Bus interface







