dNTP
Introduction
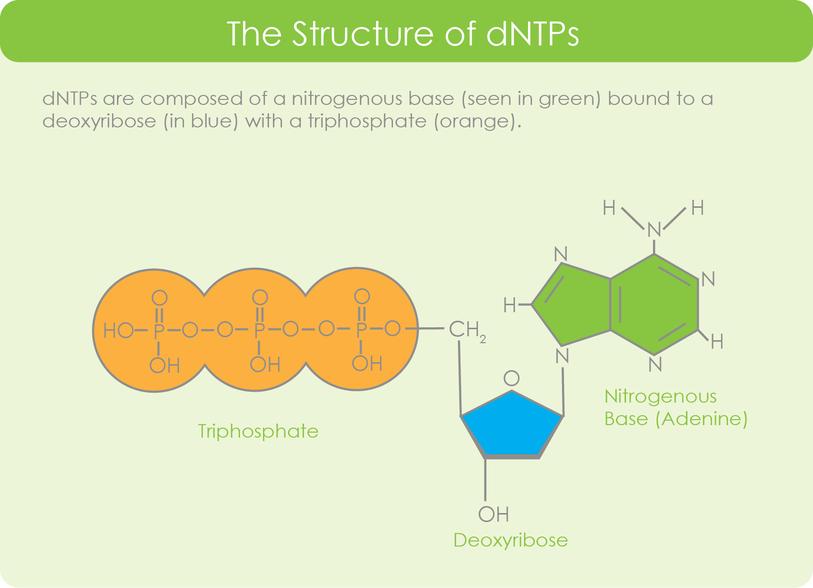
DNTP represents triphosphate of deoxyribonucleotide. Each DNTP consists of a phosphate group, a deoxyribon, and a nitrogen-containing base. There are four different DNTPs, which can be divided into two groups: purine and pyrimidine.
呤
DATP (Demodoxate 5'-triphosphate) and DGTP (deoxyguanine 5'-triphosphate) are constituted.
Adenine and guanine are the matrix in the sputum, each has a bicyclic structure.
Pyrimidine
DTTP (deoxythrosylide 5'-triphosphate) and DCTP (deoxycytidin 5'-triphosphate) constituted pyrimidine.
Thymidine and cytosine are characteristics in pyrimidine, each having a single loop structure.
DNA Structure
DNA double helix structure consisting of DNTP, very similar to the monomer unit in the polymer. If you unlock DNA and imagine it is a step, the phosphate group is alternately constitutes both sides of the ladder, (only "skeleton skeleton", the base will form a ladder. An important feature of DNA is that the two bases form a step by hydrogen bond connection. This combination will remain together with two DNA chains. Pyrimidine cannot be paired, and the purity can not be paired. The base pair can only be carried out between TA or GC. This is found by Erwin Chargaff. In his experiment, he extracted DNA from the nucleus and recorded the amount of four nucleotides present. He found that the percentage of T is always equal to the percentage of A. The same relationship was found between G and C. He also found that a percentage of A or T added to 100% percentage of g or c. These findings greatly helped Watson, Crek, Franklin and Wilkins.
Hydrogen bond
g and C bases There is only three hydrogen bonds, but there is only two hydrogen bonds between the A and T base. There are only two forms between
a and t, as the adenine base has less electrocondosition than the hydrogen attached, and therefore does not generate δ negative charges thereon. It means that oxygen on the carbon 2 of thymus cannot form a hydrogen bond thereof. hydrogen.
Thus, this means that more thermal energy is needed to make DNA degeneration, which is more rich than the AT-rich DNA.
forming DNA backbone
As previously mentioned, the main chain of DNA is composed of alternating phosphoric acid and deoxyribon groups. The bond formed between adjacent nucleotides on one chain of DNA is a phosphate diester bond. A 5 'or 3' carbon atom of a deoxyrose is formed in combination with the oxygen bonding of the first phosphate. This is a condensation reaction removed from each nucleotide. This is why nucleotides found in DNA are actually DNMPS (deoxyribonucleotide monophosphate).
Storage
DNTP is dissolved in NaOH storage liquid having a pH 7.0, the initial reservoir can be diluted to 10 mol / L, and stored in the -20 ° C refrigerator after dispensing. DNTP uses a concentration between 20 to 200 μmol / L. The four DNTPs must work with other concentrations to reduce mismatch errors.
Using the concentration of
In the PCR reaction, the low DNTP concentration can be used to reduce nucleotide erroneous incorporation when the non-target position start and extension. The minimum DNTP concentration can generally be determined according to the length and composition of the target sequence. For example, in a 100 μl reaction system, the concentration of 4 DNTPs is 20 μmol / L, which may substantially satisfy the synthesis 2.6 μg of DNA or 10 pMol/L / L / L / L / L.
Latest: National Super Computing Tianjin Center
Next: Service labor







