Chemical elements
Cognitivehistory
Historicalorigins
Theoriginofelementalthinkingisveryearly,theBabyloniansAndtheancientEgyptiansonceregardedwater(laterairandsoil)asthemainconstituentelementsoftheworld,formingthetheoryofthreeelements.TheancientIndianshadfourmajortheories,andtheancientChinesehadthetheoryofthefiveelements.
Thedoctrineofelements,thatis,thedoctrineoftreatingelementsasthesimplestcomponentofallrealobjectsinnature,hasbeenproducedsinceancienttimes.However,themodernnotionthatelementswereregardedasaconcreteformofmatterdidnotexistinancienttimes.WhetherinancientChinesephilosophyorinancientIndianorWesternphilosophy,elementsareregardedasanexpressionofabstractandprimitivespirit,orthebasicnatureofmatter.
AncientGreeknaturalphilosophyputforwardthefamousfour-elementtheory.ThiswasnotcreatedbyGreekphilosophers.ThetheoryofthefourelementsexistedinthetraditionalfolkbeliefsofancientGreece,butitdidnothavea(relativelyspeaking)solidtheoreticalsystemsupport.AncientGreekphilosophers"borrowed"theconceptsoftheseelementsasessence.
Chemicalelements(49photos)
TheMilesianphilosopherThalesadvocatedthattheessenceofallthingsiswater,andonlywateristheessence,earthandairThesetwoelementsarecondensationorthinningofwater.Anaximanderchangedtheessencetoaprimitivesubstance(called"infinite"or"indeterminate"),andaddedthefourthelementoffire.Afterthefourelementsareformedfromthisprimitivesubstance,theyaredividedintofourlayersintheorderofearth,water,air,andfire.Thefireevaporateswaterandproducesland,andthewatervaporrisestoenclosethefireinacirculartubeofcloudandmist.Whatpeopleseeascelestialbodiesistheholesofthesetubes,sothatwecanseethefireinside.Formedtheearliestembryonicformofthefourelements.Anaximenes,anotherMilesianphilosopher,regardedairorairasprimitivematter,andsaidthatotherelementswerecomposedofair.Whentheairbecomesthinner,itbecomesafire.Hisargumentisthattheairexhaledfromthemouthishot,butwhenitcomesoutunderpressure,itfeelscold.Similarly,throughtheprocessofcondensation,airfirstbecomeswaterandthenearth.Thedifferencebetweentheseelementsisonlytheresultofquantitativechanges,andtheelementsarejustaircondensedorthinnedtovaryingdegrees.
Intheearlydays,philosophersheadedbytheMiliSchoolofInspectoratemostlytookasingleelementastheiressence.ItwasnotuntilEmpedoclesthatthefour-elementcoexistencephilosophicalsystemwasestablishedforthefirsttime.Somepeoplearguedthatthiswasthefirstattempt.Toexplainthetraditionalfour-elementtheoryinascientificway,butjudgingfromtheincompleteliteratureleftbyEmpedokler,thistheorydoesnothaveenoughevidencetosupportit.Empedoclerusedtheterm"root"(Greek:ῥιζὤματα)inhisbook"OnNature"about450BC.Empedoklerwasthefirstpersontosystematicallyputforwardthetheoryoffourelements.Hebelievesthatallthingsarecomposedoffourmaterialelements:earth,air,water,andfire.Theseelementsexistforever,andtheyareconnectedorseparatedbytheothertwoabstractelements,loveandhate.
Democritusbelievesthattheoriginofeverythingisatomandvoid.Atomsarethelastindivisibleparticlesofmatter.Everythingintheuniverseismadeupofatomsmovinginthevoid.Theso-calledcreationofthingsisthecombinationofatoms.Theatomisineternalmotion,thatis,motionisinherenttotheatomitself.Voidisabsoluteemptiness,aplacewhereatomsmove.
Thewell-knowntheoryofthefourelementswaslaterputforwardbyAristotle.HistheorydidnotincludethetwoabstractelementsofloveandhateinEmpedocler’stheory,butbelievedthatThesefourelementshavethenatureofbeingopposedtoeachother.Itisfurtherdeducedthattheoriginsofallthingsintheworldarefourprimitiveproperties:cold,heat,dry,andwet,andtheelementsarecomposedoftheseprimitivepropertiescombinedindifferentproportions.Aristotleconceivedthetheoryoffiveelementsin"OntheSky"andotherworks,addingether(essence,eternity)toPlato'sfourelements.Aristotlebelievedthat"thereisnovoidseparatedfrommatter"and"thereisnovoidintheobject".Aristotle'sformaldefinitionof"element"canbefoundinMetaphysics.
Moderndevelopment
Whetheritisancientnaturalphilosophers,alchemists,orancientmedicalscientists,theirunderstandingofelementsisthroughobservationofobjectivethingsOritwassolvedbyspeculation.Itwasonlyinthemiddleofthe17thcenturythatduetotheriseofscientificexperiments,someexperimentaldataonmaterialchangeswereaccumulated,andtheconceptofelementswasinitiallysolvedfromtheresultsofchemicalanalysis.
In1661,BritishscientistBoyleexpresseddoubtsaboutthefourelementsofAristotleandthethreeoriginalsofalchemists,andpublishedabookletof"ScepticalChemists".
Boyleemphasizedtheimportanceofexperimentationwhenaffirmingandexplainingwhichsubstancesareprimitiveandsimple.Hecalledthosesubstancesthatcouldnolongerbedecomposedsimplesubstances,thatis,elements.
Foralongperiodoftimethereafter,elementsareconsideredtobesimplesubstancesthatcannotbesubdividedbychemicalmethods.Thisconfusesorequatesthetwoconceptsofelementandsimplesubstance.
Moreover,inthelaterperiod,duetothelackofpreciseexperimentalmaterials,whichsubstancesshouldbeattributedtochemicalelements,orwhichsubstancesaresimplesubstancesthatcannotbesubdivided,thisquestionalsofailed.Getresolved.
Lavoisierlistedhislistofchemicalelementsinhisbook"TheBasicsofChemistry"publishedin1789.Atotalof33chemicalelementswerelisted,dividedinto4categories:
1.Simplesubstancesbelongingtothegaseousstatecanbeconsideredaselements:light,heat,oxygen,nitrogen,andhydrogen.
2.Simplenon-metallicsubstancesthatcanoxidizeandformacids:sulfur,phosphorus,carbon,hydrochloricacid,hydrofluoricacid,andboricacid.
3.Simplemetalsubstancesthatcanoxidizeandformsalts:antimony,arsenic,silver,cobalt,copper,tin.Iron,manganese,mercury,molybdenum,gold,platinum,lead,tungsten,zinc.
4.Simplesoilthatcanformsalt:lime,bittersoil,heavysoil,bauxite,andsilica.
Fromthislistofchemicalelements,itcanbeseenthatLavoisiernotonlylistssomenon-elementalsubstancesaselements,butalsoregardslightandheataselements.
ThereasonwhyLavoisierlistshydrochloricacid,hydrofluoricacidandboricacidaselementsisbasedonhisowntheorythatallacidscontainoxygen.Hydrochloricacid,hethinksitisacompoundofhydrochloricacidandoxygen,thatis,itisacompoundofsimplesubstanceandoxygen,soheconsidershydrochloricacidtobeachemicalelement.Thesameistrueforhydrofluoricacidgroupsandboronicacidgroups.Thereasonwhyheadded"thatcanoxidizeandformacid"before"simplenon-metallicsubstance"isalsointhis.Inhisopinion,sinceitcanbeoxidized,ofcourseitcanbecomeacid.
Asforthe"soilquality"inLavoisier'stableofelements,beforethe19thcentury,theywereconsideredelementsbythechemistryresearchersatthetime,andtheyweresimplesubstancesthatcouldnotbefurtherdivided."Earth"atthetimemeantsimplesubstanceswithsuchcommonproperties,suchasalkaline,noteasilymeltedwhenheated,didnotundergochemicalchanges,hardlydissolvedinwater,anddidnotproducebubbleswhenencounteredwithacid.Inthisway,lime(calciumoxide)isakindofsoil,heavysoil-bariumoxide,bittersoil-magnesia,silica-silica,alumina-alumina.Todaytheyareoxidesofalkalineearthelementsorearthelements.This"earth"characteralsocomesfromtheatomtheory.
Atthebeginningofthe19thcentury,thetalentedBritishscientistDavidenteredtheRoyalAcademytopresideoverscientificlectures.Afterthelecture,hedevotedalotoftimetoscientificresearchandwasthefirsttoinventthemethodofextractingelementalmetalelementsbyelectrolysis.Usingthismethod,hewascalledthescientistwhodiscoveredthemostelementsatthattime.Inordertoextractpotassiumandsodium,Davidwasevenblindedbychemicals.
Atthebeginningofthe19thcentury,Daltonestablishedtheatomictheoryinchemistryandsetouttodeterminetheatomicweight.)Amountofatomsofthesamekind.
In1841,Bezieriusbasedonthefactthatsomeelements,suchassulfurandphosphorus,canexistindifferentforms.Sulfurhasrhombohedralsulfurandmonoclinicsulfur,andphosphorushaswhitephosphorusandredphosphorus.,Createdtheconceptofhomo(element)elementheteromorphism,thatis,thesameelementcanformdifferentelements.Thisshowsthattheconceptsofelementandsimplesubstancearedifferentandnotthesame.
Inthesecondhalfofthe19thcentury,duringthetimewhenMendeleevestablishedtheperiodicsystemofchemicalelements,itwasclearlypointedoutthatthebasicpropertyofelementswasatomicweight.Hebelievesthatthedifferencesbetweentheelementsareconcentratedinthedifferentatomicweights.Heproposedthattwodifferentconceptsshouldbedistinguishedbetweenelementalandelemental.Hepointedoutthattherearenometallicmercuryandgaseousoxygeninredmercuryoxide,butelementalmercuryandelementaloxygen,whichappearasmetalsandgaseswhentheyexistaselementalsubstances.
However,withthedevelopmentofsocialproductivityandtheadvancementofscienceandtechnology,attheendofthe19thcentury,electrons,X-raysandradioactivitywerediscoveredoneafteranother,leadingscientiststostudythestructureofatoms.In1913,BritishchemistSodiproposedtheconceptofisotope.Isotopesareforeignbodiesofthesameelementwiththesamenuclearchargebutdifferentatomicweights.Theyarelocatedinthesamesquarepositionintheperiodictableofchemicalelements.
Intheory,therearemanyelementsintheperiodictableofchemicalelementsthatneedtobesupplemented.Theseventhcycleshouldhave32elements,whiletheeighthcyclethathasnotyetbeendiscoveredshouldhave50elements.Therefore,theelementcycleneedstobecontinuouslysupplementedandimproved.
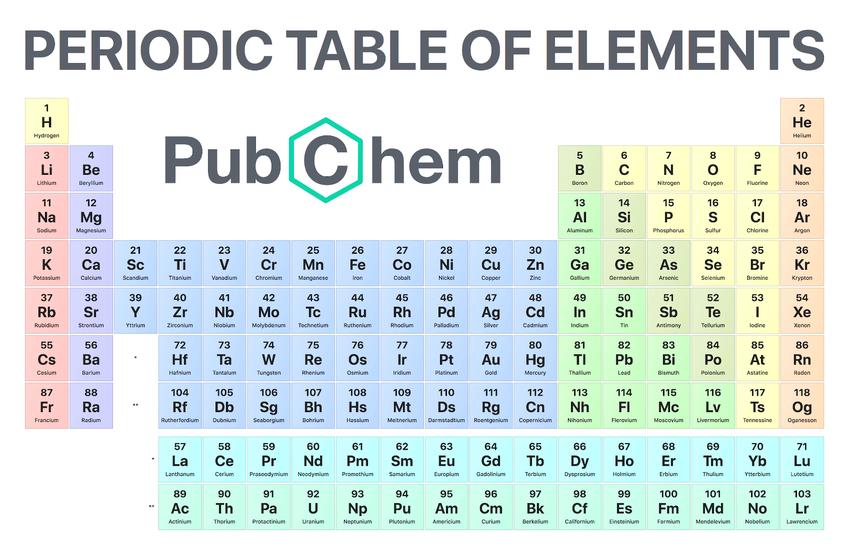
PeriodicTableofElements
ⅠA | ⅡA | ⅢB | ⅣB | ⅤB | ⅥB | ⅦB | Ⅷ | ⅠB | ⅡB | ⅢA | ⅣA | ⅤA | ⅥA | ⅦA | 0 | ||
1 H Hydrogen | 2 He Helium | p>||||||||||||||||
3 Li lithium | 4 Be Beryllium | 5 B Boron | 6 C Carbon | 7 N Nitrogen | 8 O Oxygen | 9 F Fluorine | 10 Ne Neon | ||||||||||
11 Na Sodium | 12 Mg Mg | 13 Al Aluminum | 14 Si Silicon | 15 P P | 16 S Sulfur | 17 Cl Chlorine | 18 Ar Argon | ||||||||||
19 K Potassium | 20 Ca Calcium | 21 Sc Sc | 22 Ti Titanium | 23 V Vanadium | 24 Cr Chromium | 25 Mn Manganese | 26 Fe Iron | 27 Co Cobalt | 28 Ni Nickel | 29 Cu Copper | 30 Zn Zinc | 31 Ga Gallium | 32 Ge Ge | 33 As Arsenic | 34 Se Selenium | 35 Br Bromo | 36 Kr 氪 |
37 Rb Rb | 38 Sr Strontium | 39 Y Yttrium | 40 Zr Zirconium | 41 Nb Niobium | 42 Mo Molybdenum | 43 Tc Technetium | 44 Ru Ruthenium | 45 Rh Rhodium | 46 Pd Palladium | 47 Ag Silver | 48 Cd Cadmium | 49 In Indium | 50 Sn Tin | 51 Sb Antimony | 52 Te Tellurium | 53 I Iodine | 54 Xe Xenon |
55 Cs Cesium | 56 Ba Barium | 57~71 Lanthanide | 72 Hf Hf | 73 Ta Tantalum | 74 W Tungsten | 75 Re Ren | 76 Os Os | 77 Ir Iridium | 78 Pt Platinum | 79 Au Gold | 80 Hg Mercury | 81 Tl Thallium | 82 Pb Lead | 83 Bi Bismuth | 84 Po Poly | 85 At 砹 | 86Rn Radon |
87 Fr Franium | 88 Ra Ra | 89~103 Actinide | 104 Rf 𬬻 | 105 Db 𬭊 | 106 Sg 𬭳 | 107 Bh 𬭛 | 108 Hs 𬭶 | 109 Mt 鿏 | 110 Ds 𫟼 | 111 Rg 𬬭 | 112 Cn 鎶 | 113 Nh 鉨 | 114 Fl 𫓧 | 115 Mc 镆 | 116 Lv 鉝 | 117 Ts Ishida | 118 Og Qiao |
Lanthanide | 57 La Lanthanum | 58 Ce Ce | 59 Pr Pr | 60 Nd Neodymium | 61 Pm Promethium | 62 Sm Sm | 63 Eu Eu | 64 Gd Gadolinium | 65 Tb Terbium | 66 Dy Dy | 67 Ho Ho | 68 Er Er | 69 Tm Thu p> | 70 Yb Ytterbium | 71 Lu Lutetium |
Actinide p> | 89 Ac Actin | 90 Th Th | 91 Pa 钍 p> | 92 U uranium | 93 Np Neptunium | 94 Pu Plutonium | 95 Am Americium | 96 Cm 锔 | 97 Bk 锫 | 98 Cf 锎 | 99 Es 锿 | 100 Fm Fen | 101 Md 钔 | 102 No 锘 | 103 Lr 铹 |
Note:Duetothereasonthatthefontcannotbedisplayedonsomedevices,elements112to113and116aredisplayedintraditionalcharacters.
Simplifiedcharactersare钅哥,钅尔,and钅立inorder.
TheperiodictableoftheelementswasfirstcreatedbytheRussianscientistDmitriMendeleevin1869.Later,aftermanyyearsofrevisionbymanyscientists,thecontemporaryperiodictablewasformed.Thereare118elementsintheperiodictable.Eachelementhasanumberwhosesizeisexactlyequaltothenumberofprotonsinthenucleusoftheelement’satom.Thisnumberiscalledtheatomicnumber.Thearrangementandpropertieshaveobviousregularity.Scientistsarrangetheelementswiththesamenumberofelectronsinthesamerowandtheelementswiththesamenumberofelectronsintheoutermostlayerinthesamecolumnaccordingtotheincreasingatomicnumber.
Theperiodictableofelementshas7periodsand17groups.Eachhorizontalrowiscalledacycle,andeachverticalrowiscalledafamily.These7cyclescanbedividedintoshortcycles(1,2,3)andlongcycles(4,5,6,7).Thereare17groups,namely:alkalimetals,alkalineearthmetals,rareearthmetals,titaniumgroupelements,vanadiumgroupelements,chromiumgroupelements,manganesegroupelements,irongroupmetals,platinumgroupmetals,currencymetals,zincgroupelements,borongroupElement,carbongroupelement,phosphoruselement,chalcogenelement,halogenelement,raregaselement.Thepositionofanelementintheperiodictablenotonlyreflectstheatomicstructureoftheelement,butalsoshowstheevolutionarylawofelementpropertiesandtheinternalconnectionbetweenelements.
Inthesameperiod,fromlefttoright,thenumberofelectronlayersoutsidetheelementcoreisthesame,thenumberofelectronsintheoutermostlayerincreasessequentially,andtheatomicradiusdecreases(exceptforelementsofgroupzero).Theabilitytoloseelectronsgraduallyweakens,theabilitytogainelectronsgraduallyincreases,themetallicitygraduallyweakens,andthenon-metallicitygraduallyincreases.Thehighestpositiveoxidationnumberofelementsincreasesfromlefttoright(exceptforthosewithoutpositivevalence),andthelowestnegativeoxidationnumberincreasesfromlefttoright(exceptforthefirstcycle,exceptforOandFelementsinthesecondcycle).
Inthesamefamily,fromtoptobottom,thenumberofelectronsintheoutermostlayeristhesame,thenumberofelectronlayersoutsidethecoregraduallyincreases,theatomicnumberincreases,themetallicityoftheelementsincreases,andthenon-metallicitydecreases.
Themeltingpointofmetalsinthesamegroupdecreasesfromtoptobottom,andthehardnessdecreases,andthemeltingpointofthemaingroupmetalsinthesameperiodincreasesfromlefttoright,andthehardnessincreases.
Theperiodictableofelementsisofgreatsignificance.Scientistsusethistofindnewelementsandcompounds.
Worldview
Domestic
From403BCto221BC,sometheoriesabouttheoriginofeverythingappearedinmycountryduringtheWarringStatesPeriod,Asthe"LaoZiDaodeJing"wrote:"Taobegetsone,onelifetwo,twobegetsthree,threebegetsallthings."Anotherexampleisthe"Guanzi·Shuidi"said:"Whereisthewater?Theoriginofallthingsisalso."
ThetheoryoftheFiveElementsinourcountryhasmaterialmeaning,butsometimesitappearsasabasicnature.ThetheoryoftheFiveElementsinourcountryfirstappearedinthe"ShangShu"attheendoftheWarringStatesPeriod.Theoriginaltextis:"TheFiveElements:Oneiswater,twoisfire,threeiswood,fourisgold,andfiveisearth.Woodmeansstraight,goldmeansleather,andearthmeansJiahu."Translatedintotoday’slanguageis:"Fiveelements:oneiswater,theotherisfire,thethirdiswood,thefourthisgold,andthefifthisearth.Thenatureofwatermoisturizesthings.Downward,thenatureoffireburnsupward.Thenatureofwoodcanbecurvedorstraight,thenatureofgoldcanbemeltedandtransformed,andthenatureofsoilcanbecultivatedandharvested."Inthelater"Mandarin",thefiveelementsclearlyexpresstheprimitivenessofallthings.theconceptof.Theoriginaltextis:"Ahusbandandarealcreature,iftheyarethesame,theywillnotcontinue.Heequalshimastheharmony,soitcangrowandgrow.Ifthesamebarnyardisthesame,allisabandonment.Therefore,thefirstkingusedearthandgoldandwood.Hundredsofthingsarecombinedwithwater,fireandwater.”Thetranslationis:“Harmonyistheprincipleofcreatingthings,andthesamecannotcontinueforever.Combiningmanydifferentthingstogethertobalancethemiscalledharmony.,Soitcanmakethematerialrichandgrow.Ifthesamethingsareaddedtogether,theywillbediscarded.Therefore,thepastemperorsusedearthandmetal,wood,water,andfiretocombinewitheachothertocreateeverything."
Westernnaturalschool
13-14thcentury,westernalchemistsaddedthreeelementstotheelementsproposedbyAristotle:Mercury,sulfurandsalt.Thisiswhatthealchemistscallthethreeoriginals.However,themercury,sulphur,andsalttheysaidonlyshowedthepropertiesofmatter:mercury-theembodimentofmetallicproperties,sulfur-theembodimentofflammabilityandnon-metallicproperties,andtheembodimentofsaltsolubility.
Bythe16thcentury,theSwissphysicianParacelsappliedthethreeoriginalsofalchemiststohismedicine.Heproposedthatmatteriscomposedofthreeelements—salt(body),mercury(soul)andsulfur(spirit)indifferentproportions.Thecauseofdiseaseisthelackofoneofthethreeelementsintheorganism.Inordertohealthedisease,itisnecessarytoinjectthemissingelementsintothehumanbody.
1 | H | Hydrogen | 1.00794(7) | In1766,BritisharistocratHenryCavendish(1731-1810)discovered |
2 | He | Helium | 4.002602(2) | In1868,theFrenchastronomerJeanson(1824-1907)andtheBritishastronomerNormanLocker(1836-1920)usedthesolarspectrumtodiscover. |
3 | Li | Lithium | 6.941(2) | In1817,theSwedeJohnOggsAffweson(1792-1841)discoveredwhenanalyzingfeldspar |
4 | Be | Beryllium | 9.012182(3) | 1798,FrenchLouisNicolasWalkeran(1763-1829)discoveredwhenanalyzingberyl |
5 | ||||
5 | B | Boron | 10.811(7) | In1808,FrenchmanJosephLouisLussac(1788-1850)andFrenchmanLouisTayKnar(1777-1857)collaboratedonthediscovery,andtheBritishchemistDavidpublisheditonly9dayslate |
6 | C | Carbon | 12.011 | In1796,BritishchemistSmithsonTenant(1761-1815)discovereddiamondsComposedofcarbonatoms |
7 | N | Nitrogen | 14.007 | In1772,theSwedishchemistKarlWilhelmSchelerTogetherwithFrenchchemistLavaJieandScottishchemistDanielRutherford(1749-1819)discoverednitrogenatthesametime |
8 | O | Oxygen | 15.999 | In1771,itwasdiscoveredbyPriestleyinEnglandandSchelerinSweden;ancientChinesescientistsMaHefound(controversial) |
9 | F | Fluorine | 18.998 | In1786,chemistspredictedtheexistenceoffluorine.In1886,FrenchchemistMoissanproducedfluorinegasbyelectrolysis. |
10 | Ne | Neon | 20.17 | 1898,BritishChemistryLamseyandRayleighfound |
11 | Na | Sodium | 22.9898 | In1807,BritishchemistDaviddiscoveredandprepareditbyelectrolysis |
12 | Mg | Mg | 24.305 | In1808,BritishchemistDaviddiscoveredandprepareditbyelectrolysis |
13 | Al | Aluminum | 26.982 | In1825,DanishHCOerstedusedanhydrousaluminumchlorideandpotassiumamalgamtoevaporateAfterremovingmercury |
14 | Si | Silicon | 28.085 | In1823,theSwedishchemistBezeniusdiscovereditasanelement |
15 | P | P | 30.974 | In1669,theGermanPolantdiscoveredbyevaporatingurine |
16 | S | Sulfur | 32.06 | Theancientsdiscovered(Lavoisier,Francedeterminedittobeanelement) |
17 | Cl | Chlorine | 35.453 | In1774,theSwedishchemistSchelerdiscoveredchlorine.In1810,Davidpointedoutthatitwasanelement. |
18 | Ar | Argon | 39.94 | In1894,BritishchemistsRayleighandLimseydiscovered |
19 | K | K | 39.098 | In1807,theBritishchemistDaviddiscoveredandusedelectrolysistomakeGet |
20 | Ca | Calcium | 40.08 | In1808,BritishchemistDaviddiscoveredandprepareditbyelectrolysis |
21 | Sc | Sc | 44.956 | In1879,theSwedishNelsondiscovered |
22 | Ti | Titanium | 47.9 | 1791,BritishMarkGreeGorediscoveredfromtheore |
23 | V | Vanadium | 50.94 | In1831,itwasdiscoveredwhenSurfsterwood,Swedenwasresearchingyellowleadmine.In1867,Rost,England,madevanadiummetalforthefirsttime |
24 | Cr | Chrome | 51.996 | In1797,FrenchLouisNicolasWalkerindiscoveredwhenanalyzingchromium-leadore |
25 | Mn | Mn | 54.938 | 1774,Scheler,SwedenFoundfrompyrolusite |
26 | Fe | 铁 | 55.845 | Ancientdiscovery |
27 | Co | Cobalt | 58.9332 | In1735,Brandtdiscovered |
28 | Ni | Nickel | 58.69 | TheancientChinesediscoveredandusedit.In1751,theSwedishmineralogistKronstadtfirstthoughtitwasanelement |
29 | Cu | Copper | 63.54 | Discoveredbyancients |
30 | Zn | Zinc | 65.38 | DiscoveryofancientChinese |
31 | Ga | Gallium | 69.72 | 1875,BoisBoudran,FranceDiscoveredwhenstudyingsphalerite |
32 | Ge | Ge | 72.5 | In1885,Winkler,Germanydiscovered |
33 | As | Arsenic | 74.922 | In317AD,Gehong,China,wasmadefromacombinationofrealgar,turpentine,andsaltpeter,andlaterconfirmedbyLavoisier,FranceIsanewelement |
34 | Se | Selenium | 78.9 | In1817,itwasdiscoveredbyBezenius,Sweden |
35 | Br | Bromo | 79.904 | 1824,Bari,FranceAldiscovery |
36 | Kr | 氪 | 83.8 | LemseyandRayleighdiscoveredin1898 |
37 | Rb | Rb | 85.467 | In1860,GermanBunsenandKirchhoffusedspectralanalysistodiscover |
38 | Sr | Strontium | 87.62 | 1808,EnglandChemistDaviddiscoveredandmadeitbyelectrolysis |
39 | Y | Yttrium | 88.906 | In1789,Klaprut,Germanydiscovered |
40 | Zr | Zirconium | 91.22 | In1789,GermanchemistKlaprosdiscoveredinzircon |
41 | Nb | Niobium | 92.9064 | In1801,BritishchemistHatchettdiscovered |
42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 95.94 | Swedishhousein1778Lediscoveredthatin1883,theSwedishGellmwasthefirsttomakeit |
43 | Tc | Technetium | 97.907 | In1937,LawrenceoftheUnitedStatesusedacyclotrontoobtainitforthefirsttime,anditwasidentifiedasanewelementbyPerrierofItalyandSibourgoftheUnitedStates.Itisthefirstartificialelementmanufactured |
44 | Ru | ruthenium | 101.1 | 1827years,theRussianOlympicChanfoundinplatinumoresinUkrainein1844RussiaKlausgoldalsofounditandrecognizedasanewelement |
45 | Rh | Rh | 102.906 | 1803,theBritishWollastonfoundfromthecrudeandseparatingtheplatinum |
46 | Pd | Pd | 106.42 | 1803,theBritishWollastonfoundfromthecrudeandseparatingtheplatinum |
47 | Ag | silver | 107.868 | ancientfound |
48 | Cd | Cd | 112.41 | 1817years,F.施特罗迈尔foundfromzinccarbonate |
49 | In | indium | 114.82 | 1863,theGermaninHittfoundbyspectralanalysisandLex |
50 | Sn | tin | 118.6 | ancientfound |
51 | Sb | antimony | 121.7 | ancientfound |
52 | Te | Te | 127.6 | 1782Nian,FJMillerReichenbachSteinfoundingold-bearingore |
53 | I | iodo | 126.905 | 1814,theFrenchKuwatewa(1777-1838)foundthat,afterconfirmationbytheBritishandFrenchDavidGuyLussacresearchisanewelement |
54 | Xe | Xe | 131.3 | 1898,theBritishRamplugandRayleighfound |
55 | Cs | cesium | 132.905 | 1860,theGermanBunsenandKirchhoffspectroscopicallyanalysisfound |
56 | Ba | barium | 137.33 | 1808,BritishchemistDaviddiscoveredandprepared |
57~71 | La~Lu | lanthanide | ||
57 | La | lanthanum | 138.9 | 1839,theSwedishMoShanGill(1797-1858)discoveredfromceriumnitrateincrude |
58 | Ce | Ce | 140.1 | 1803,theSwedishminingshellArrheniusGermanKlaproth,Sweden,Greece,Georgiawerediscovered |
59 | Pr | Pr | 140.9 | 1885,theAustrianWeiSiba(1858-1929)separatedroseBengalpullneodymiumsaltandgreensaltfrompraseodymium,neodymium,praseodymiummixturewasfoundtobe |
60 | Nd | neodymium | 144.2 | 1885,theAustrianWeiSiba(1858-1929)PrNdpullseparatedfromthemixtureofneodymiumsaltsandrosegreenpraseodymiumsaltfound |
61 | Pm | Pm | (147) | 1945,theUnitedStatesmariinskiy,GlenDeningandKeLiningfoundfromthereactoruraniumfissionproductatomsandseparating |
62 | Sm | Sm | 150.3 | 1879,theFrenchboisBodeLongfound |
63 | Eu | Eu | 151.96 | 1896,theFrenchfoundcoverdelMar |
64 | Gd | Gd | 157.25 | 1880yearsSwissMarignacSamaMagnitogorskfoundfromore.In1886,FranceBoisbaudranmadeoutofpuregadolinium |
65 | Tb | Tb | 158.9 | 1843,theSwedishMosangdeerfoundthatin1877officiallynamed |
66 | Dy | dysprosium | 162.5 | 1886,theFrenchBoisbaudranfound,1906FrenchUrbainmademorepuredysprosium |
67 | Ho | holmium | 164.9 | 1879,theSwedishCliveseparatedfromthesoilanddiscoveredEr |
68 | Er | erbium | 167.2 | 1843,theSwedishModesangerbyfractionalprecipitationmethodfoundfromyttriumsoil |
69 | Tm | Tm | 168.9 | 1879,theSwedishCliveseparatedfromthesoilanddiscoveredEr |
70 | Yb | Yb | 173.04 | 1878,found瑞士马里尼Senanayake |
71 | Lu | lutetium | 174.967 | 1907yearsWels,AustriaandFrancepullUrbainfound |
Hf | hafnium | 178.4 | 1923,theSwedishandDutchchemistHevesyphysicistsfoundKoster | |
73 | Ta | Ta | 180.947 | 1802,theSwedishinsuranceIkefoundthatin1844GermanyRothfirstniobium,tantalumseparate |
74 | W | W | 183.8 | 1781yearsSwedenScheelefoundexplodedacid |
75 | Re | Re | 186.207 | 1925,theGermangeochemistNoddackcouplefromplatinummineWefound |
76 | Os | Os | 190.2 | 1803,BritishchemistTennantetalfoundthat |
| 77 | Ir | iridium | 192.2 | 1803,BritishchemistTennantetalfoundthatwhenusingaquaregiaplatina |
78 | Pt | platinum | 195.08 | 1735,theSpanishAntonioPintofoundWuluoAriverofgold,the1748BritishchemistW.Watsonrecognizedasanewelement |
79 | Au | gold | 196.967 | ancientfound |
80 | Hg | Hg | 200.5 | TheancientGreeksfound |
81 | Tl | Tl | 1861,theBritishCrooksfoundbyspectralanalysis | |
82 | Pb | lead | 207.2 | ancientfound |
83 | Bi | bismuth | 208.98 | 1450,theGermanValentinfound |
84 | Po | polonium | (209) | 1898,theFrenchPierreCuriediscovered |
85 | At | astatine | (201) | 1940,theAmericanchemistXigeLei,Corsonetalbismuthtargetbombardedwithparticlestofindandobtainα- |
86 | Rn | radon | (222) | 1903,theBritishLamsafound |
87 | Fr | francium | (223) | 1939,theFrenchPerretchemist(F)unexpecteddiscovery |
88 | Ra | Ra | 226.03 | 1898,theFrenchchemistPierreCuriediscovered,1910MarieCuriemadeofametalradium |
89~103 | Ac~Lr | actinide | ||
89 | Ac | actinide | (227) | 1899,theFrenchDerbyALElfounduraniumslagandisolated |
90 | Th | Th | 232.0 | 1828inSwedenTonyminingArrheniusdiscovered |
91 | Pa | protactinium | 231.03588(2) | 1917years,F.Soddy,J.Gladstone,D.Hahn,L.Meitnerfoundindependently |
92 | U | U | 238.0 | 1789,theGermanKlaproth(1743-1817)discovered,in1842itwasmadeofmetaluranium |
93 | Np | Np | 237.05 | 1940,theUnitedStatesandAbeWilsonMacmillanlikeartificialnuclearreactionobtainedwith |
94 | Pu | Pu | 244.06 | 1940,theUnitedStatesSeaborg,KennedyandWalterfound |
| 95 | Am | Am | (243) | 1944,theUnitedStatesandJiaoSuoetSeaborgplutoniumatomsbyprotonbombardmenttoobtain |
96 | Cm | Cm | (247) | 1944,theUnitedStatesandotherartificialSeaborgandJiaoSuoprepared |
97 | Bk | berkelium | (247) | 1949yearsibid. |
98 | Cf | cf | (251) | 1950yearsibid. |
99 | Es | einsteinium | 252.08 | isgenerated1952,U.S.JiaoSuoobservationheighthydrogenbombfound |
100 | atomic"debris" Fm | fermium | 257.10 | 1952yearsibid. |
101 | Md | mendelevium | 258.10 | In1955,theUnitedStatesandotherJiaoSuobombardmenteinsteiniumwithheliumnucleiprepared |
102 | No | Nuo | 259.10 | 1958years,theNobelInstituteincooperationwiththeSwedishUniversityofCalifornia,bombardingcuriumwithcarbonionsobtained |
103 | Lr | andrhodium | 262 | 1961years,theUniversityofCaliforniascientistsboronatombombardingcaliforniummade |
104 | Rf | furnace | 261.11 | 1964,theRussianVladimirLiaoLoveandJiaoSuoUS-ledscienceteamareeachmadeofartificial |
105 | Db | JinDu | 262.11 | 1967yearsibid. |
Sg | Jinhi | 263.12 | 1974,theRussianVladimirLiaoLovethelikewithchromiumnuclearbombardmentcoremadeoflead,thesameyearintheUnitedStatesJiaoSuo,etalSeaborganotherwayalsobeprepared | |
107 | Bh | Jin-wave | 264.12 | 1981discovered,bytheDanishphysicistBohrnamed |
108 | Hs | Jinblack | 273 | 1984discovered |
109 | Mt | Jinwheat | 268 | 1982datedFederalRepublicofGermany.8yearsDamushitaGSIassociationwithbismuthiron-58109-209weresynthesizedinaparticleacceleratorelement |
110 | Ds | Jinup | (269) | 1994November9heavyionResearchInstituteinDarmstadt,Germanyfound |
111 | Rg | JinLun | (272) | GermaninternationalresearchgroupCenterforheavyionResearchProfessorSylvesterGoodeHoffmanledin1994firstdiscovered |
112 | Cn | JinColumbia | (277) | in1996wassynthesized |
113 | Nh | Ni | (278) | toSeptember28,2004,wasdiscoveredinJapanInstituteofPhysics,LanzhouInstituteofModernPhysics,ChineseUniversity,ChineseAcademyofSciencesInstituteofHighEnergy |
114 | Fl | Fu | (289) | EluosifuLiaoLuofulaboratorynuclearreactioninsynthesis2000 |
115 | Mc | ROBOT | (288) | February2,2004,bythe俄罗斯杜布纳jointInstitutefornuclearResearchandtheUSLawrenceLivermorenationallaboratorycoalitionscientificteamsuccessfullysynthesized |
116 | Lv | Li | (289) | Lawrence-LivermoreNationalLaboratoryin2004synthesis |
117 | Ts | Ishida | (291) | thiselementfirstsuccessfulsynthesisof2010,2012successfullysynthesizedagain. 俄罗斯杜布纳JointInstituteforNuclearResearchSynthesis |
118 | Og | gasAustrian | (294) | UnitedsynthesizedbyscientistsatLawrenceLivermorenationallaboratoryandthejointInstituteofNuclearResearchof俄罗斯杜布纳 |
isotopic
Afterthat,theBritishphysicistAstonprovethatmostofthechemicalelementshavedifferentisotopesinearly1921.Atomicmassisotopeelementbyisotopesexistinnaturethemassfractionoftheaveragevalueobtained.
inthissameperiodin1913BritishphysicistMoseleystudysystematicallywavelengthresultingcathodemadeofvariouselementsoftheX-ray,atomicelementofstatedfeaturesofthiselementthenuclearcharge,whichislaterdeterminedbyatomicnumber.
Thus,iftheisotopeconsideredseveraldifferentindividualelements,itisobviouslyunreasonable.Becausethefeatureisnotdeterminedatomicweightofatomicelements,butitsnuclearcharge.
1923,theInternationalCommissiondecisionatomicweight:atomicchemicalelementisonemethodofclassificationaccordingtothenumberofnuclearcharge,thesamechargeofauditingaclassofatomsknownasanelement.
elementDevelopment
historicaldevelopment
ancient | C | \ |
ancient | sulfur | \ |
ancient | Fe | \ |
ancient | copper | \ |
ancient | zinc | \ |
ancient | silver | \ |
ancient | tin | \ |
ancient | antimony | \ |
ancient | gold | \ |
ancient | Hg | \ |
ancient | lead | \ |
1250 | arsenic | (Germany)MagnusNice(A.Magnus,1193-1280) |
1669 | P | (Germany)Portland(H.Brand) |
1735 | cobalt | (Sweden)Brent(G.Brandt,1694-1768) |
1735 | platinum | (West)Germany-Ulloa(DAdeUlloa,1716-1795) |
1751 | Ni | (Sweden)SEKstater(AFCronsted,1722-1765) |
1753 | bismuth | (England)ocherFremont(CJGeoffory) |
1766 | hydrogen | (England)Cavendish(H.Cavendish,1731-1810) |
1772 | nitrogen | (England)Rutherford(D.Rutherford,1749-1819) |
1774 | oxygen | (England)PulieSiTerry(J.Priestley,1733-1804) |
1774 | chloro | (Sweden)Scheele(CWScheele,1742-1780) |
1774 | Mn | (Sweden)Gunn(JGGahn,1745-1818) |
1778 | molybdenum | (Sweden)Elm(PJHjelm,1746-1813) |
1782 | Te | (Austria)Muller(FJMüller,1740-1825) |
1783 | W | (West)Germany-el-WuYaSeoul(deElhuyar)brothers |
1789 | Be | (method)WokeLan(LNVauquelin) |
1789 | zirconium | (Germany)Klaproth(MHKlaproth,1743-1817) |
1789 | U | (Germany)Klaproth(MHKlaproth) |
1791 | titanium | (England)GolayGore(W.Gregor,1762-1817) |
1794 | yttrium | (Finland)Gadolin(J.Gadolin,1760-1852) |
1798 | chromium | (method)WokeLan(LNVauquelin,1763Year-1829) |
1801 | niobium | (English)Hatchett(C.Hatchett,1765?-1847) |
1802 | Ta | (Sweden)Edinburghgrams(AGEkeberg,1767-1813) |
1803 | Rh | (England)WuRuston(WHWollaston,1766-1828) |
1803 | Pd | (England)WuRuston(WHWollaston) |
1803 | Ce | (Germany)Klaproth(MHKlaproth)et |
1804 | iridium | (England)Knightstation(S.Tennant) |
1804 | Os | (England)Knightstation(S.Tennant,1761-1815) |
1807 | boron | (France)cover-Lussac(JLGay-Lussac,1778-1850),etc. |
1807 | sodium | (English)David(H.Davy,1778-1829) |
1807 | K | (England)Dave(H.Davy) |
1808 | magnesium | (England)Dave(H.Davy) |
1808 | calcium | (England)Dave(H.Davy)et |
1808 | Sr | (England)Dave(H.Davy) |
1808 | barium | (England)Dave(H.Davy) |
1811 | iodo | (method)KuteWa(JBCourtois,1777-1838) |
1817 | lithium | (Sweden)阿尔费德森(JAArfredson,1792-1841) |
1817 | Cd | (Germany)施特罗迈尔(F.Stromeyer,1776-1835) |
1818 | Se | (Sweden)Berzelius(JJBerzelius,1779-1848) |
1823 | silicon | (Sweden)Berzelius(JJBerzelius) |
1824 | bromo | (method)Bala(AJBalard,1802-1876) |
1827 | Al | (Dan)OscarTed(HCOersted,1777-1851) |
1828 | Th | (Sweden)Berzelius(JJBerzelius) |
1830 | vanadium | (Sweden)SeFusiTom(NGSefstrom,1787-1845) |
1839 | lanthanum | (Sweden)Mosangdeer(CGMosander,1797-1858) |
1843 | Tb | (Sweden)Mosangdeer(CGMosander) |
1843 | Er | (Sweden)Mosangdeer(CGMosander) |
1844 | ruthenium | (Russia)Klaus(KKKlaus,1796-1864) |
1860 | cesium | (Germany)Bunsen(RWBunsen,1811-1899),etc. |
1861 | Rb | (Germany)Bunsen(RWBunsen)et |
1861 | Tl | (England)Crooks(W.Crookes,1832-1919) |
1863 | indium | (Germany)Reich(F.Reich,1799-1882)andother |
1875 | gallium | (France)de-Boisbaudran(L.deBoisbaudran,1838-1912) |
1878 | Yb | (Switzerland)Marleysodiumg(JCGMarignac) |
1879 | Sc | (Sweden)Nelson(LFNilson,1840-1899) |
1879 | Sm | (France)de-Boisbaudran(L.deBoisbaudran) |
1879 | holmium | (Sweden)Cliff(PTCleve,1840-1905) |
1879 | Tm | (Sweden)Cliff(PTCleve,1840-1905) |
1880 | Gd | (Switzerland)Marleysodiumg(JCGMarignac,1817-1894) |
1885 | Pr | (Austria)von-WeissBach(BAvonWeisbach,1858-1929) |
1885 | neodymium | (Austria)von-WeissBach(BAvonWeisbach) |
1886 | fluoro | (France)mauvoisin(H.Moissan,1852-1907)* |
1886 | Ge | (Germany)Winkler(CAWinkler,1838-1904) |
1886 | dysprosium | (France)de-Boisbaudran(L.deBoisbaudran) |
1894 | Ar | (England)Rayleigh(RJSRayleigh,1842-1919),etc.* |
1895 | helium` | (England)Ramsey(W.Ramsay,1852-1916)* |
1898 | polonium` | (method)Curie(MarieCurie,1867-1934)(borninPoland),etc.* |
1898 | Ra | (method)Curie(MarieCurie),etc. |
1898 | Ne | (England)Ramsey(W.Ramsay)like |
1898 | krypton` | (England)Ramsey(W.Ramsay)et |
1898 | Xe | (England)Ramsey(W.Ramsay)et |
1899 | actinide | (France)DerbyBernard(ALDebierne,1874-1949) |
1900 | Radon | (Germany),Dawn(FEDorn) |
1901 | Eu | (France)deVersailles(EADemaroay,1852-1904) |
1905 | lutetium | (France)Urbain(G.Urbain,1872-?) |
1913 | protactinium | (波兰)法扬斯(K.Fajans,1887-?) |
1923 | 铪 | (匈)冯-海维塞(G.vonHevesey)等 |
1925 | 铼 | (德)诺达克(W.Noddack)等 |
1937 | 锝 | (意)塞格瑞(B.Segré)等 |
1939 | 钫 | (法)佩丽(MMPerey) |
1939 | 镎 | (美)麦克米兰(EMMcMillan,1907-1991)等* |
1940 | 砹 | (美)柯尔森(DRCorson)等 |
1940 | 钚 | (美)西伯格(GTSeaborg,1912-1999)等* |
1947 | 钷 | (美)马林斯基(J.A.Marinsky,1919-?) |
现代发展
当然,至今人们对化学元素的认识过程也没有完结。当前化学中关于分子结构的研究,物理学中关于核粒子的研究等都在深入开展,可以预料它将带来对化学元素的新认识。到2007年为止,总共有118种元素被发现,其中94种是存在于地球上。
Latest: Relay circuit
Next: Ledger








